After-sales Service Provided: Free spare parts
Warranty: 3 years
Type: Fan Parts
Application: Commercial, Household
Power Source: Electric
Model Number: ZG-BS-D03
Product name: Fan Spare Parts, Fan Gearbox
Use: Wall shake head Fan
Material: ABS & POM
Certification: ISO9 sets Plastic gearbox/day.
Our Company Factory8sets/day Workshop34 Injection Molding Machines, also have Wire Cutting Machine, EDM, Precision Lathe, Hobbing Machine.
WarehouseLarge and independent storage space,all raw material with ROTH certification
TeamTop class expers & scholars to do designs and Production,with strict quality control system Packing & Delivery Packing: 200pcs or 600pcs in a waterproof PO bag then in 1 carton. we can do packing according to customer’s requirement.
Our Certifications We have ISO9001 CERTIFICATION. We have lots of Patent certificate such as for Fan Gearbox, auto brush gearbox, bike adjusting seat, Mower pulley Compatible with Exmark 106-2175, 132-9420 Toro 106-2175, Toro TimeCutter SS 3200, TimeCutter SS 3216 and coffer maker gearbox.
Customer Photo Favorable CommentWe have been working together for 7 years.
Skilltrans factory is It’s a trustworthy factory.
Favorable CommentFive years of cooperation is very pleasant, from raw materials to products Skilltrans factory have strict quality control system, best is their delivery time is stable.
Favorable CommentWe have cooperated for 9 years and have become good friends. We will continue to cooperate.
FAQ 1, Why choose us?12years experience of plastic gearbox making factoryReal manufacturer can guarantee on time delivery & low costFast & professional reply, latest answer is within 24 hours2,Can you do OEM?Yes, 1 of our advantages is we have experts and scholars to do designs, develops. Welcome OEM, ODM3, How long is guarantee time?3 years for all the products,not contain artificial damage4, Can we get sample?Yes, usually sample is free, we need you cooperate to pay shipping charges5, How can you control the quality?We have gear measuring center, CMMs and other inspection equipment,All the products need pass 100% check before delivery.6, Can you do our packing and delivery time?Yes, usually our packing is 1 piece in 1 bag,600pcs in 1 carton. delivery time is 20-28days7,How to pay?Usually 30% deposit, Factory price good quality soap extruded machine stainless steel duplex single worm vacuum plodder the rest paid before shipment skilltrans catalogue pricelist win win contact

Hypoid Bevel Vs Straight Spiral Bevel – What’s the Difference?
Spiral gears come in many different varieties, but there is a fundamental difference between a Hypoid bevel gear and a Straight spiral bevel. This article will describe the differences between the two types of gears and discuss their use. Whether the gears are used in industrial applications or at home, it is vital to understand what each type does and why it is important. Ultimately, your final product will depend on these differences.
Hypoid bevel gears
In automotive use, hypoid bevel gears are used in the differential, which allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds while maintaining the vehicle’s handling. This gearbox assembly consists of a ring gear and pinion mounted on a carrier with other bevel gears. These gears are also widely used in heavy equipment, auxiliary units, and the aviation industry. Listed below are some common applications of hypoid bevel gears.
For automotive applications, hypoid gears are commonly used in rear axles, especially on large trucks. Their distinctive shape allows the driveshaft to be located deeper in the vehicle, thus lowering the center of gravity and minimizing interior disruption. This design makes the hypoid gearset one of the most efficient types of gearboxes on the market. In addition to their superior efficiency, hypoid gears are very easy to maintain, as their mesh is based on sliding action.
The face-hobbed hypoid gears have a characteristic epicycloidal lead curve along their lengthwise axis. The most common grinding method for hypoid gears is the Semi-Completing process, which uses a cup-shaped grinding wheel to replace the lead curve with a circular arc. However, this method has a significant drawback – it produces non-uniform stock removal. Furthermore, the grinding wheel cannot finish all the surface of the tooth.
The advantages of a hypoid gear over a spiral bevel gear include a higher contact ratio and a higher transmission torque. These gears are primarily used in automobile drive systems, where the ratio of a single pair of hypoid gears is the highest. The hypoid gear can be heat-treated to increase durability and reduce friction, making it an ideal choice for applications where speed and efficiency are critical.
The same technique used in spiral bevel gears can also be used for hypoid bevel gears. This machining technique involves two-cut roughing followed by one-cut finishing. The pitch diameter of hypoid gears is up to 2500 mm. It is possible to combine the roughing and finishing operations using the same cutter, but the two-cut machining process is recommended for hypoid gears.
The advantages of hypoid gearing over spiral bevel gears are primarily based on precision. Using a hypoid gear with only three arc minutes of backlash is more efficient than a spiral bevel gear that requires six arc minutes of backlash. This makes hypoid gears a more viable choice in the motion control market. However, some people may argue that hypoid gears are not practical for automobile assemblies.
Hypoid gears have a unique shape – a cone that has teeth that are not parallel. Their pitch surface consists of two surfaces – a conical surface and a line-contacting surface of revolution. An inscribed cone is a common substitute for the line-contact surface of hypoid bevel gears, and it features point-contacts instead of lines. Developed in the early 1920s, hypoid bevel gears are still used in heavy truck drive trains. As they grow in popularity, they are also seeing increasing use in the industrial power transmission and motion control industries.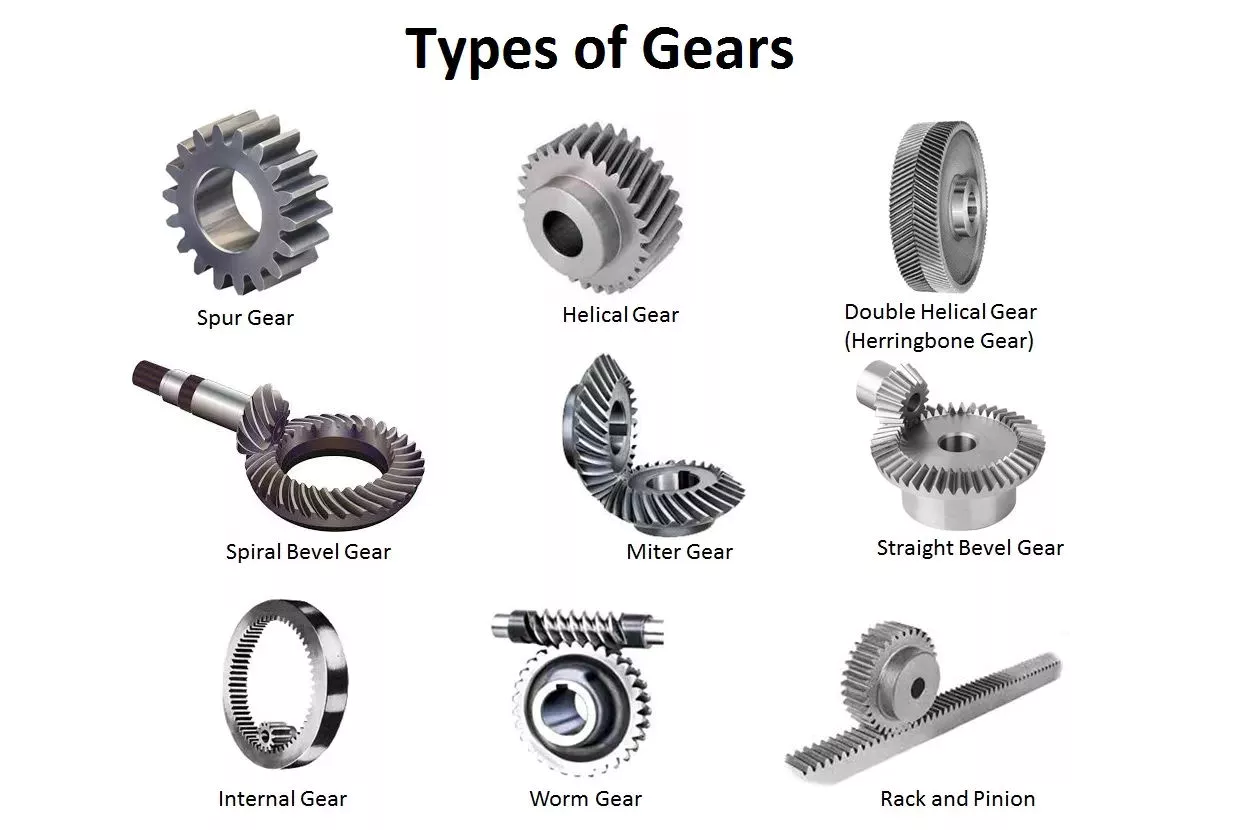
Straight spiral bevel gears
There are many differences between spiral bevel gears and the traditional, non-spiral types. Spiral bevel gears are always crowned and never conjugated, which limits the distribution of contact stress. The helical shape of the bevel gear is also a factor of design, as is its length. The helical shape has a large number of advantages, however. Listed below are a few of them.
Spiral bevel gears are generally available in pitches ranging from 1.5 to 2500 mm. They are highly efficient and are also available in a wide range of tooth and module combinations. Spiral bevel gears are extremely accurate and durable, and have low helix angles. These properties make them excellent for precision applications. However, some gears are not suitable for all applications. Therefore, you should consider the type of bevel gear you need before purchasing.
Compared to helical gears, straight bevel gears are easier to manufacture. The earliest method used to manufacture these gears was the use of a planer with an indexing head. However, with the development of modern manufacturing processes such as the Revacycle and Coniflex systems, manufacturers have been able to produce these gears more efficiently. Some of these gears are used in windup alarm clocks, washing machines, and screwdrivers. However, they are particularly noisy and are not suitable for automobile use.
A straight bevel gear is the most common type of bevel gear, while a spiral bevel gear has concave teeth. This curved design produces a greater amount of torque and axial thrust than a straight bevel gear. Straight teeth can increase the risk of breaking and overheating equipment and are more prone to breakage. Spiral bevel gears are also more durable and last longer than helical gears.
Spiral and hypoid bevel gears are used for applications with high peripheral speeds and require very low friction. They are recommended for applications where noise levels are essential. Hypoid gears are suitable for applications where they can transmit high torque, although the helical-spiral design is less effective for braking. For this reason, spiral bevel gears and hypoids are generally more expensive. If you are planning to buy a new gear, it is important to know which one will be suitable for the application.
Spiral bevel gears are more expensive than standard bevel gears, and their design is more complex than that of the spiral bevel gear. However, they have the advantage of being simpler to manufacture and are less likely to produce excessive noise and vibration. They also have less teeth to grind, which means that they are not as noisy as the spiral bevel gears. The main benefit of this design is their simplicity, as they can be produced in pairs, which saves money and time.
In most applications, spiral bevel gears have advantages over their straight counterparts. They provide more evenly distributed tooth loads and carry more load without surface fatigue. The spiral angle of the teeth also affects thrust loading. It is possible to make a straight spiral bevel gear with two helical axes, but the difference is the amount of thrust that is applied to each individual tooth. In addition to being stronger, the spiral angle provides the same efficiency as the straight spiral gear.
Hypoid gears
The primary application of hypoid gearboxes is in the automotive industry. They are typically found on the rear axles of passenger cars. The name is derived from the left-hand spiral angle of the pinion and the right-hand spiral angle of the crown. Hypoid gears also benefit from an offset center of gravity, which reduces the interior space of cars. Hypoid gears are also used in heavy trucks and buses, where they can improve fuel efficiency.
The hypoid and spiral bevel gears can be produced by face-hobbing, a process that produces highly accurate and smooth-surfaced parts. This process enables precise flank surfaces and pre-designed ease-off topographies. These processes also enhance the mechanical resistance of the gears by 15 to 20%. Additionally, they can reduce noise and improve mechanical efficiency. In commercial applications, hypoid gears are ideal for ensuring quiet operation.
Conjugated design enables the production of hypoid gearsets with length or profile crowning. Its characteristic makes the gearset insensitive to inaccuracies in the gear housing and load deflections. In addition, crowning allows the manufacturer to adjust the operating displacements to achieve the desired results. These advantages make hypoid gear sets a desirable option for many industries. So, what are the advantages of hypoid gears in spiral gears?
The design of a hypoid gear is similar to that of a conventional bevel gear. Its pitch surfaces are hyperbolic, rather than conical, and the teeth are helical. This configuration also allows the pinion to be larger than an equivalent bevel pinion. The overall design of the hypoid gear allows for large diameter shafts and a large pinion. It can be considered a cross between a bevel gear and a worm drive.
In passenger vehicles, hypoid gears are almost universal. Their smoother operation, increased pinion strength, and reduced weight make them a desirable choice for many vehicle applications. And, a lower vehicle body also lowers the vehicle’s body. These advantages made all major car manufacturers convert to hypoid drive axles. It is worth noting that they are less efficient than their bevel gear counterparts.
The most basic design characteristic of a hypoid gear is that it carries out line contact in the entire area of engagement. In other words, if a pinion and a ring gear rotate with an angular increment, line contact is maintained throughout their entire engagement area. The resulting transmission ratio is equal to the angular increments of the pinion and ring gear. Therefore, hypoid gears are also known as helical gears.


editor by Cx 2023-07-06
China 22mm 12v 24V dc planetary gear motor with encoder spiral bevel gear
Error:获取返回内容失败,
Your session has expired. Please reauthenticate.

Benefits and Uses of Miter Gears
If you’ve ever looked into the differences between miter gears, you’re probably wondering how to choose between a Straight toothed and Hypoid one. Before you decide, however, make sure you know about backlash and what it means. Backlash is the difference between the addendum and dedendum, and it prevents jamming of the gears, protects the mating gear surfaces, and allows for thermal expansion during operation.
Spiral bevel gears
Spiral bevel gears are designed to increase efficiency and reduce cost. The spiral shape creates a profile in which the teeth are cut with a slight curve along their length, making them an excellent choice for heavy-duty applications. Spiral bevel gears are also hypoid gears, with no offsets. Their smaller size means that they are more compact than other types of right-angle gears, and they are much quieter than other types of gear.
Spiral bevel gears feature helical teeth arranged in a 90-degree angle. The design features a slight curve to the teeth, which reduces backlash while increasing flexibility. Because they have no offsets, they won’t slip during operation. Spiral bevel gears also have less backlash, making them an excellent choice for high-speed applications. They are also carefully spaced to distribute lubricant over a larger area. They are also very accurate and have a locknut design that prevents them from moving out of alignment.
In addition to the geometric design of bevel gears, CZPT can produce 3D models of spiral bevel gears. This software has gained widespread attention from many companies around the world. In fact, CZPT, a major manufacturer of 5-axis milling machines, recently machined a prototype using a spiral bevel gear model. These results prove that spiral bevel gears can be used in a variety of applications, ranging from precision machining to industrial automation.
Spiral bevel gears are also commonly known as hypoid gears. Hypoid gears differ from spiral bevel gears in that their pitch surface is not at the center of the meshing gear. The benefit of this gear design is that it can handle large loads while maintaining its unique features. They also produce less heat than their bevel counterparts, which can affect the efficiency of nearby components.
Straight toothed miter gears
Miter gears are bevel gears that have a pitch angle of 90 degrees. Their gear ratio is 1:1. Miter gears come in straight and spiral tooth varieties and are available in both commercial and high precision grades. They are a versatile tool for any mechanical application. Below are some benefits and uses of miter gears. A simple explanation of the basic principle of this gear type is given. Read on for more details.
When selecting a miter gear, it is important to choose the right material. Hard faced, high carbon steel is appropriate for applications requiring high load, while nylon and injection molding resins are suitable for lower loads. If a particular gear becomes damaged, it’s advisable to replace the entire set, as they are closely linked in shape. The same goes for spiral-cut miter gears. These geared products should be replaced together for proper operation.
Straight bevel gears are the easiest to manufacture. The earliest method was using an indexing head on a planer. Modern manufacturing methods, such as the Revacycle and Coniflex systems, made the process more efficient. CZPT utilizes these newer manufacturing methods and patented them. However, the traditional straight bevel is still the most common and widely used type. It is the simplest to manufacture and is the cheapest type.
SDP/Si is a popular supplier of high-precision gears. The company produces custom miter gears, as well as standard bevel gears. They also offer black oxide and ground bore and tooth surfaces. These gears can be used for many industrial and mechanical applications. They are available in moderate quantities from stock and in partial sizes upon request. There are also different sizes available for specialized applications.
Hypoid bevel gears
The advantages of using Hypoid bevel and helical gears are obvious. Their high speed, low noise, and long life make them ideal for use in motor vehicles. This type of gear is also becoming increasingly popular in the power transmission and motion control industries. Compared to standard bevel and helical gears, they have a higher capacity for torque and can handle high loads with less noise.
Geometrical dimensioning of bevel/hypoid bevel gears is essential to meet ANSI/AGMA/ISO standards. This article examines a few ways to dimension hypoid bevel and helical gears. First, it discusses the limitations of the common datum surface when dimensioning bevel/helical gear pairs. A straight line can’t be parallel to the flanks of both the gear and the pinion, which is necessary to determine “normal backlash.”
Second, hypoid and helical gears have the same angular pitch, which makes the manufacturing process easier. Hypoid bevel gears are usually made of two gears with equal angular pitches. Then, they are assembled to match one another. This reduces noise and vibration, and increases power density. It is recommended to follow the standard and avoid using gears that have mismatched angular pitches.
Third, hypoid and helical gears differ in the shape of the teeth. They are different from standard gears because the teeth are more elongated. They are similar in appearance to spiral bevel gears and worm gears, but differ in geometry. While helical gears are symmetrical, hypoid bevel gears are non-conical. As a result, they can produce higher gear ratios and torque.
Crown bevel gears
The geometrical design of bevel gears is extremely complex. The relative contact position and flank form deviations affect both the paired gear geometry and the tooth bearing. In addition, paired gears are also subject to process-linked deviations that affect the tooth bearing and backlash. These characteristics require the use of narrow tolerance fields to avoid quality issues and production costs. The relative position of a miter gear depends on the operating parameters, such as the load and speed.
When selecting a crown bevel gear for a miter-gear system, it is important to choose one with the right tooth shape. The teeth of a crown-bevel gear can differ greatly in shape. The radial pitch and diametral pitch cone angles are the most common. The tooth cone angle, or “zerol” angle, is the other important parameter. Crown bevel gears have a wide range of tooth pitches, from flat to spiral.
Crown bevel gears for miter gear are made of high-quality materials. In addition to metal, they can be made of plastic or pre-hardened alloys. The latter are preferred as the material is less expensive and more flexible than steel. Furthermore, crown bevel gears for miter gears are extremely durable, and can withstand extreme conditions. They are often used to replace existing gears that are damaged or worn.
When selecting a crown bevel gear for a miter gear, it is important to know how they relate to each other. This is because the crown bevel gears have a 1:1 speed ratio with a pinion. The same is true for miter gears. When comparing crown bevel gears for miter gears, be sure to understand the radii of the pinion and the ring on the pinion.
Shaft angle requirements for miter gears
Miter gears are used to transmit motion between intersecting shafts at a right angle. Their tooth profile is shaped like the mitre hat worn by a Catholic bishop. Their pitch and number of teeth are also identical. Shaft angle requirements vary depending on the type of application. If the application is for power transmission, miter gears are often used in a differential arrangement. If you’re installing miter gears for power transmission, you should know the mounting angle requirements.
Shaft angle requirements for miter gears vary by design. The most common arrangement is perpendicular, but the axes can be angled to almost any angle. Miter gears are also known for their high precision and high strength. Their helix angles are less than ten degrees. Because the shaft angle requirements for miter gears vary, you should know which type of shaft angle you require before ordering.
To determine the right pitch cone angle, first determine the shaft of the gear you’re designing. This angle is called the pitch cone angle. The angle should be at least 90 degrees for the gear and the pinion. The shaft bearings must also be capable of bearing significant forces. Miter gears must be supported by bearings that can withstand significant forces. Shaft angle requirements for miter gears vary from application to application.
For industrial use, miter gears are usually made of plain carbon steel or alloy steel. Some materials are more durable than others and can withstand higher speeds. For commercial use, noise limitations may be important. The gears may be exposed to harsh environments or heavy machine loads. Some types of gears function with teeth missing. But be sure to know the shaft angle requirements for miter gears before you order one.


editor by Cx 2023-06-28
China 0414.2023-1.75M-36Z aodisi custom grinding spur gear bevel spiral gear
Issue: New
Guarantee: 6 Months
Shape: Rack Equipment, custom made gear
Relevant Industries: Developing Substance Outlets, Producing Plant, Machinery Repair Retailers, Construction works , wholesale hip hop gold hollow rope chain rope chain au750 18k CZPT gold wholesale 18k gold necklace rope chain Power & Mining, Other, Energy transmission components, distinct kind of sector
Excess weight (KG): 50
Showroom Area: None
Video outgoing-inspection: Provided
Machinery Test Report: Offered
Advertising and marketing Type: New Product 2571
Warranty of main parts: 1 Year
Main Elements: Gear
Product Variety: 571.2571-1.75M-36Z spur equipment
Content: 20CrMnTi
Normal or Nonstandard: Normal
Pressure Angle: 20 Degree
Tooth of treatment: milled
Facet Floor: Included
Merchandise Identify: gear
Tape: spur equipment
Hardness: Heat treatment method
Packaging Details: Normal CZPT worthy bundle
Port: HangZhou
Personalize Precision Spur Gear 1.75M-36Z
Warm Tip: The value of the earlier mentioned products is inaccurate. Please contact us for consultation on the specific value. We sincerely search CZPT to your contact!
| Solution name | products equipment rack |
| Edge | Specialist, MONDE PC205710 Excavator mulcher attachment tree root crushing Versatile, Higher High quality |
| Materials | Metal |
| Tooth of remedy | Milled |
| Facet Floor | Incorporated |
| Date of delivery | 20-sixty times right after payment |
| Packing | Regular CZPT worthy package |
| Heat Idea | The above item picture price is only for reference, particular cost please contact seek the advice of ation, sincerely look CZPT to your contact! |
Sizzling sale
Speak to us
Business Information
Shipping

Benefits and Uses of Miter Gears
If you’ve ever looked into the differences between miter gears, you’re probably wondering how to choose between a Straight toothed and Hypoid one. Before you decide, however, make sure you know about backlash and what it means. Backlash is the difference between the addendum and dedendum, and it prevents jamming of the gears, protects the mating gear surfaces, and allows for thermal expansion during operation.
Spiral bevel gears
Spiral bevel gears are designed to increase efficiency and reduce cost. The spiral shape creates a profile in which the teeth are cut with a slight curve along their length, making them an excellent choice for heavy-duty applications. Spiral bevel gears are also hypoid gears, with no offsets. Their smaller size means that they are more compact than other types of right-angle gears, and they are much quieter than other types of gear.
Spiral bevel gears feature helical teeth arranged in a 90-degree angle. The design features a slight curve to the teeth, which reduces backlash while increasing flexibility. Because they have no offsets, they won’t slip during operation. Spiral bevel gears also have less backlash, making them an excellent choice for high-speed applications. They are also carefully spaced to distribute lubricant over a larger area. They are also very accurate and have a locknut design that prevents them from moving out of alignment.
In addition to the geometric design of bevel gears, CZPT can produce 3D models of spiral bevel gears. This software has gained widespread attention from many companies around the world. In fact, CZPT, a major manufacturer of 5-axis milling machines, recently machined a prototype using a spiral bevel gear model. These results prove that spiral bevel gears can be used in a variety of applications, ranging from precision machining to industrial automation.
Spiral bevel gears are also commonly known as hypoid gears. Hypoid gears differ from spiral bevel gears in that their pitch surface is not at the center of the meshing gear. The benefit of this gear design is that it can handle large loads while maintaining its unique features. They also produce less heat than their bevel counterparts, which can affect the efficiency of nearby components.
Straight toothed miter gears
Miter gears are bevel gears that have a pitch angle of 90 degrees. Their gear ratio is 1:1. Miter gears come in straight and spiral tooth varieties and are available in both commercial and high precision grades. They are a versatile tool for any mechanical application. Below are some benefits and uses of miter gears. A simple explanation of the basic principle of this gear type is given. Read on for more details.
When selecting a miter gear, it is important to choose the right material. Hard faced, high carbon steel is appropriate for applications requiring high load, while nylon and injection molding resins are suitable for lower loads. If a particular gear becomes damaged, it’s advisable to replace the entire set, as they are closely linked in shape. The same goes for spiral-cut miter gears. These geared products should be replaced together for proper operation.
Straight bevel gears are the easiest to manufacture. The earliest method was using an indexing head on a planer. Modern manufacturing methods, such as the Revacycle and Coniflex systems, made the process more efficient. CZPT utilizes these newer manufacturing methods and patented them. However, the traditional straight bevel is still the most common and widely used type. It is the simplest to manufacture and is the cheapest type.
SDP/Si is a popular supplier of high-precision gears. The company produces custom miter gears, as well as standard bevel gears. They also offer black oxide and ground bore and tooth surfaces. These gears can be used for many industrial and mechanical applications. They are available in moderate quantities from stock and in partial sizes upon request. There are also different sizes available for specialized applications.
Hypoid bevel gears
The advantages of using Hypoid bevel and helical gears are obvious. Their high speed, low noise, and long life make them ideal for use in motor vehicles. This type of gear is also becoming increasingly popular in the power transmission and motion control industries. Compared to standard bevel and helical gears, they have a higher capacity for torque and can handle high loads with less noise.
Geometrical dimensioning of bevel/hypoid bevel gears is essential to meet ANSI/AGMA/ISO standards. This article examines a few ways to dimension hypoid bevel and helical gears. First, it discusses the limitations of the common datum surface when dimensioning bevel/helical gear pairs. A straight line can’t be parallel to the flanks of both the gear and the pinion, which is necessary to determine “normal backlash.”
Second, hypoid and helical gears have the same angular pitch, which makes the manufacturing process easier. Hypoid bevel gears are usually made of two gears with equal angular pitches. Then, they are assembled to match one another. This reduces noise and vibration, and increases power density. It is recommended to follow the standard and avoid using gears that have mismatched angular pitches.
Third, hypoid and helical gears differ in the shape of the teeth. They are different from standard gears because the teeth are more elongated. They are similar in appearance to spiral bevel gears and worm gears, but differ in geometry. While helical gears are symmetrical, hypoid bevel gears are non-conical. As a result, they can produce higher gear ratios and torque.
Crown bevel gears
The geometrical design of bevel gears is extremely complex. The relative contact position and flank form deviations affect both the paired gear geometry and the tooth bearing. In addition, paired gears are also subject to process-linked deviations that affect the tooth bearing and backlash. These characteristics require the use of narrow tolerance fields to avoid quality issues and production costs. The relative position of a miter gear depends on the operating parameters, such as the load and speed.
When selecting a crown bevel gear for a miter-gear system, it is important to choose one with the right tooth shape. The teeth of a crown-bevel gear can differ greatly in shape. The radial pitch and diametral pitch cone angles are the most common. The tooth cone angle, or “zerol” angle, is the other important parameter. Crown bevel gears have a wide range of tooth pitches, from flat to spiral.
Crown bevel gears for miter gear are made of high-quality materials. In addition to metal, they can be made of plastic or pre-hardened alloys. The latter are preferred as the material is less expensive and more flexible than steel. Furthermore, crown bevel gears for miter gears are extremely durable, and can withstand extreme conditions. They are often used to replace existing gears that are damaged or worn.
When selecting a crown bevel gear for a miter gear, it is important to know how they relate to each other. This is because the crown bevel gears have a 1:1 speed ratio with a pinion. The same is true for miter gears. When comparing crown bevel gears for miter gears, be sure to understand the radii of the pinion and the ring on the pinion.
Shaft angle requirements for miter gears
Miter gears are used to transmit motion between intersecting shafts at a right angle. Their tooth profile is shaped like the mitre hat worn by a Catholic bishop. Their pitch and number of teeth are also identical. Shaft angle requirements vary depending on the type of application. If the application is for power transmission, miter gears are often used in a differential arrangement. If you’re installing miter gears for power transmission, you should know the mounting angle requirements.
Shaft angle requirements for miter gears vary by design. The most common arrangement is perpendicular, but the axes can be angled to almost any angle. Miter gears are also known for their high precision and high strength. Their helix angles are less than ten degrees. Because the shaft angle requirements for miter gears vary, you should know which type of shaft angle you require before ordering.
To determine the right pitch cone angle, first determine the shaft of the gear you’re designing. This angle is called the pitch cone angle. The angle should be at least 90 degrees for the gear and the pinion. The shaft bearings must also be capable of bearing significant forces. Miter gears must be supported by bearings that can withstand significant forces. Shaft angle requirements for miter gears vary from application to application.
For industrial use, miter gears are usually made of plain carbon steel or alloy steel. Some materials are more durable than others and can withstand higher speeds. For commercial use, noise limitations may be important. The gears may be exposed to harsh environments or heavy machine loads. Some types of gears function with teeth missing. But be sure to know the shaft angle requirements for miter gears before you order one.


editor by Cx 2023-06-19
China best Tactical Gear M16 Gun Sling Shooting Sling bevel spiral gear
Product Description
Basic data
| Name | high quality tactical gear |
| Material | 500D codura |
| Weight | 0.3kg |
| length | 1.3meter |
| Color | BK RG CB CZPT gray Mutilcam Mutilcam black AOR1 woodland Muticam tropic |
Product Description
1 High resistant to wear
2 Molle structure known for its matchless capability for accessory attachment is always a favored choice for tactical use
3 The waterproof outer cover and accessories survive all harsh weather conditions
Detail picture
Other accessories
(1)If the order is not big,door to door service by courier is OK,such as TNT, DHL,UPS,FEDEX etc.Packing Details : 1pc/bag, 40pcs/carton
(2)By air or sea as your appointed is the usual way we do, FOB port is ZheJiang or ZheJiang port.5-30 days after order
(3) If you don’t have your forwarder, we can find the cheapest
forwarder to ship the goods to your appointed port.
Q: Are you trading company or manufacturer ? A: We are factory.Q: How long is your delivery time? A: Generally it is 5-10 days if the goods are in stock. or it is 15-30 days if the goods are not in stock, it is according to quantity.Q: Do you provide samples ? is it free or extra ? A: Yes, we could offer the sample but do not free.Q: What is your terms of payment ? A: Payment=1000USD, 30% T/T in advance ,balance before shippment.
|
| Length: | 1.3meter |
|---|---|
| Material: | 500d Codura |
| Weight: | 0.3kg |
| Color: | Bk CB Cp BMC Aor1 M81 Rg Wg |
| Design: | Laser Cut |
| Other Part: | Cp |
| Samples: |
US$ 15/Set
1 Set(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Hypoid Bevel Vs Straight Spiral Bevel – What’s the Difference?
Spiral gears come in many different varieties, but there is a fundamental difference between a Hypoid bevel gear and a Straight spiral bevel. This article will describe the differences between the two types of gears and discuss their use. Whether the gears are used in industrial applications or at home, it is vital to understand what each type does and why it is important. Ultimately, your final product will depend on these differences.
Hypoid bevel gears
In automotive use, hypoid bevel gears are used in the differential, which allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds while maintaining the vehicle’s handling. This gearbox assembly consists of a ring gear and pinion mounted on a carrier with other bevel gears. These gears are also widely used in heavy equipment, auxiliary units, and the aviation industry. Listed below are some common applications of hypoid bevel gears.
For automotive applications, hypoid gears are commonly used in rear axles, especially on large trucks. Their distinctive shape allows the driveshaft to be located deeper in the vehicle, thus lowering the center of gravity and minimizing interior disruption. This design makes the hypoid gearset one of the most efficient types of gearboxes on the market. In addition to their superior efficiency, hypoid gears are very easy to maintain, as their mesh is based on sliding action.
The face-hobbed hypoid gears have a characteristic epicycloidal lead curve along their lengthwise axis. The most common grinding method for hypoid gears is the Semi-Completing process, which uses a cup-shaped grinding wheel to replace the lead curve with a circular arc. However, this method has a significant drawback – it produces non-uniform stock removal. Furthermore, the grinding wheel cannot finish all the surface of the tooth.
The advantages of a hypoid gear over a spiral bevel gear include a higher contact ratio and a higher transmission torque. These gears are primarily used in automobile drive systems, where the ratio of a single pair of hypoid gears is the highest. The hypoid gear can be heat-treated to increase durability and reduce friction, making it an ideal choice for applications where speed and efficiency are critical.
The same technique used in spiral bevel gears can also be used for hypoid bevel gears. This machining technique involves two-cut roughing followed by one-cut finishing. The pitch diameter of hypoid gears is up to 2500 mm. It is possible to combine the roughing and finishing operations using the same cutter, but the two-cut machining process is recommended for hypoid gears.
The advantages of hypoid gearing over spiral bevel gears are primarily based on precision. Using a hypoid gear with only three arc minutes of backlash is more efficient than a spiral bevel gear that requires six arc minutes of backlash. This makes hypoid gears a more viable choice in the motion control market. However, some people may argue that hypoid gears are not practical for automobile assemblies.
Hypoid gears have a unique shape – a cone that has teeth that are not parallel. Their pitch surface consists of two surfaces – a conical surface and a line-contacting surface of revolution. An inscribed cone is a common substitute for the line-contact surface of hypoid bevel gears, and it features point-contacts instead of lines. Developed in the early 1920s, hypoid bevel gears are still used in heavy truck drive trains. As they grow in popularity, they are also seeing increasing use in the industrial power transmission and motion control industries.
Straight spiral bevel gears
There are many differences between spiral bevel gears and the traditional, non-spiral types. Spiral bevel gears are always crowned and never conjugated, which limits the distribution of contact stress. The helical shape of the bevel gear is also a factor of design, as is its length. The helical shape has a large number of advantages, however. Listed below are a few of them.
Spiral bevel gears are generally available in pitches ranging from 1.5 to 2500 mm. They are highly efficient and are also available in a wide range of tooth and module combinations. Spiral bevel gears are extremely accurate and durable, and have low helix angles. These properties make them excellent for precision applications. However, some gears are not suitable for all applications. Therefore, you should consider the type of bevel gear you need before purchasing.
Compared to helical gears, straight bevel gears are easier to manufacture. The earliest method used to manufacture these gears was the use of a planer with an indexing head. However, with the development of modern manufacturing processes such as the Revacycle and Coniflex systems, manufacturers have been able to produce these gears more efficiently. Some of these gears are used in windup alarm clocks, washing machines, and screwdrivers. However, they are particularly noisy and are not suitable for automobile use.
A straight bevel gear is the most common type of bevel gear, while a spiral bevel gear has concave teeth. This curved design produces a greater amount of torque and axial thrust than a straight bevel gear. Straight teeth can increase the risk of breaking and overheating equipment and are more prone to breakage. Spiral bevel gears are also more durable and last longer than helical gears.
Spiral and hypoid bevel gears are used for applications with high peripheral speeds and require very low friction. They are recommended for applications where noise levels are essential. Hypoid gears are suitable for applications where they can transmit high torque, although the helical-spiral design is less effective for braking. For this reason, spiral bevel gears and hypoids are generally more expensive. If you are planning to buy a new gear, it is important to know which one will be suitable for the application.
Spiral bevel gears are more expensive than standard bevel gears, and their design is more complex than that of the spiral bevel gear. However, they have the advantage of being simpler to manufacture and are less likely to produce excessive noise and vibration. They also have less teeth to grind, which means that they are not as noisy as the spiral bevel gears. The main benefit of this design is their simplicity, as they can be produced in pairs, which saves money and time.
In most applications, spiral bevel gears have advantages over their straight counterparts. They provide more evenly distributed tooth loads and carry more load without surface fatigue. The spiral angle of the teeth also affects thrust loading. It is possible to make a straight spiral bevel gear with two helical axes, but the difference is the amount of thrust that is applied to each individual tooth. In addition to being stronger, the spiral angle provides the same efficiency as the straight spiral gear.
Hypoid gears
The primary application of hypoid gearboxes is in the automotive industry. They are typically found on the rear axles of passenger cars. The name is derived from the left-hand spiral angle of the pinion and the right-hand spiral angle of the crown. Hypoid gears also benefit from an offset center of gravity, which reduces the interior space of cars. Hypoid gears are also used in heavy trucks and buses, where they can improve fuel efficiency.
The hypoid and spiral bevel gears can be produced by face-hobbing, a process that produces highly accurate and smooth-surfaced parts. This process enables precise flank surfaces and pre-designed ease-off topographies. These processes also enhance the mechanical resistance of the gears by 15 to 20%. Additionally, they can reduce noise and improve mechanical efficiency. In commercial applications, hypoid gears are ideal for ensuring quiet operation.
Conjugated design enables the production of hypoid gearsets with length or profile crowning. Its characteristic makes the gearset insensitive to inaccuracies in the gear housing and load deflections. In addition, crowning allows the manufacturer to adjust the operating displacements to achieve the desired results. These advantages make hypoid gear sets a desirable option for many industries. So, what are the advantages of hypoid gears in spiral gears?
The design of a hypoid gear is similar to that of a conventional bevel gear. Its pitch surfaces are hyperbolic, rather than conical, and the teeth are helical. This configuration also allows the pinion to be larger than an equivalent bevel pinion. The overall design of the hypoid gear allows for large diameter shafts and a large pinion. It can be considered a cross between a bevel gear and a worm drive.
In passenger vehicles, hypoid gears are almost universal. Their smoother operation, increased pinion strength, and reduced weight make them a desirable choice for many vehicle applications. And, a lower vehicle body also lowers the vehicle’s body. These advantages made all major car manufacturers convert to hypoid drive axles. It is worth noting that they are less efficient than their bevel gear counterparts.
The most basic design characteristic of a hypoid gear is that it carries out line contact in the entire area of engagement. In other words, if a pinion and a ring gear rotate with an angular increment, line contact is maintained throughout their entire engagement area. The resulting transmission ratio is equal to the angular increments of the pinion and ring gear. Therefore, hypoid gears are also known as helical gears.


editor by CX 2023-06-12
China manufacturer Gtig Professional Gear Manufacturer Spur/Spiral Bevel Gear bevel spiral gear
Product Description
Product Description
| Modulo | Above 0.8 |
| Numero di Denti | Above 9teeth |
| Angolo d’Elica Helix Angle | Up to 45 |
| bore diameter | Above 6mm |
| axial length | Above 9mm |
| Gear model | Customized gear accoding to customers sample or drawing |
| Processing machine | CNC machine |
| Material | 20CrMnTi/ 20CrMnMo/ 42CrMo/ 45#steel/ 40Cr/ 20CrNi2MoA/304 stainless steel |
| Heat treattment | Carburizing and quenching/ Tempering/ Nitriding/ Carbonitriding/ Induction hardening |
| Hardness | 35-64HRC |
| Qaulity standerd | GB/ DIN/ JIS/ AGMA |
| Accuracy class | 5-8 class |
| Shipping | Sea shipping/ Air shipping/ Express |
Company Profile
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Soft Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | Internal Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Rolling Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Spur Gear |
| Material: | Stainless Steel |
| Samples: |
US$ 500/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

The Difference Between Planetary Gears and Spur Gears
A spur gear is a type of mechanical drive that turns an external shaft. The angular velocity is proportional to the rpm and can be easily calculated from the gear ratio. However, to properly calculate angular velocity, it is necessary to know the number of teeth. Fortunately, there are several different types of spur gears. Here’s an overview of their main features. This article also discusses planetary gears, which are smaller, more robust, and more power-dense.
Planetary gears are a type of spur gear
One of the most significant differences between planetary gears and spurgears is the way that the two share the load. Planetary gears are much more efficient than spurgears, enabling high torque transfer in a small space. This is because planetary gears have multiple teeth instead of just one. They are also suitable for intermittent and constant operation. This article will cover some of the main benefits of planetary gears and their differences from spurgears.
While spur gears are more simple than planetary gears, they do have some key differences. In addition to being more basic, they do not require any special cuts or angles. Moreover, the tooth shape of spur gears is much more complex than those of planetary gears. The design determines where the teeth make contact and how much power is available. However, a planetary gear system will be more efficient if the teeth are lubricated internally.
In a planetary gear, there are three shafts: a sun gear, a planet carrier, and an external ring gear. A planetary gear is designed to allow the motion of one shaft to be arrested, while the other two work simultaneously. In addition to two-shaft operation, planetary gears can also be used in three-shaft operations, which are called temporary three-shaft operations. Temporary three-shaft operations are possible through frictional coupling.
Among the many benefits of planetary gears is their adaptability. As the load is shared between several planet gears, it is easier to switch gear ratios, so you do not need to purchase a new gearbox for every new application. Another major benefit of planetary gears is that they are highly resistant to high shock loads and demanding conditions. This means that they are used in many industries.
They are more robust
An epicyclic gear train is a type of transmission that uses concentric axes for input and output. This type of transmission is often used in vehicles with automatic transmissions, such as a Lamborghini Gallardo. It is also used in hybrid cars. These types of transmissions are also more robust than conventional planetary gears. However, they require more assembly time than a conventional parallel shaft gear.
An epicyclic gearing system has three basic components: an input, an output, and a carrier. The number of teeth in each gear determines the ratio of input rotation to output rotation. In some cases, an epicyclic gear system can be made with two planets. A third planet, known as the carrier, meshes with the second planet and the sun gear to provide reversibility. A ring gear is made of several components, and a planetary gear may contain many gears.
An epicyclic gear train can be built so that the planet gear rolls inside the pitch circle of an outer fixed gear ring, or “annular gear.” In such a case, the curve of the planet’s pitch circle is called a hypocycloid. When epicycle gear trains are used in combination with a sun gear, the planetary gear train is made up of both types. The sun gear is usually fixed, while the ring gear is driven.
Planetary gearing, also known as epicyclic gear, is more durable than other types of transmissions. Because planets are evenly distributed around the sun, they have an even distribution of gears. Because they are more robust, they can handle higher torques, reductions, and overhung loads. They are also more energy-dense and robust. In addition, planetary gearing is often able to be converted to various ratios.
They are more power dense
The planet gear and ring gear of a compound planetary transmission are epicyclic stages. One part of the planet gear meshes with the sun gear, while the other part of the gear drives the ring gear. Coast tooth flanks are used only when the gear drive works in reversed load direction. Asymmetry factor optimization equalizes the contact stress safety factors of a planetary gear. The permissible contact stress, sHPd, and the maximum operating contact stress (sHPc) are equalized by asymmetry factor optimization.
In addition, epicyclic gears are generally smaller and require fewer space than helical ones. They are commonly used as differential gears in speed frames and in looms, where they act as a Roper positive let off. They differ in the amount of overdrive and undergearing ratio they possess. The overdrive ratio varies from fifteen percent to forty percent. In contrast, the undergearing ratio ranges from 0.87:1 to 69%.
The TV7-117S turboprop engine gearbox is the first known application of epicyclic gears with asymmetric teeth. This gearbox was developed by the CZPT Corporation for the Ilyushin Il-114 turboprop plane. The TV7-117S’s gearbox arrangement consists of a first planetary-differential stage with three planet gears and a second solar-type coaxial stage with five planet gears. This arrangement gives epicyclic gears the highest power density.
Planetary gearing is more robust and power-dense than other types of gearing. They can withstand higher torques, reductions, and overhung loads. Their unique self-aligning properties also make them highly versatile in rugged applications. It is also more compact and lightweight. In addition to this, epicyclic gears are easier to manufacture than planetary gears. And as a bonus, they are much less expensive.
They are smaller
Epicyclic gears are small mechanical devices that have a central “sun” gear and one or more outer intermediate gears. These gears are held in a carrier or ring gear and have multiple mesh considerations. The system can be sized and speeded by dividing the required ratio by the number of teeth per gear. This process is known as gearing and is used in many types of gearing systems.
Planetary gears are also known as epicyclic gearing. They have input and output shafts that are coaxially arranged. Each planet contains a gear wheel that meshes with the sun gear. These gears are small and easy to manufacture. Another advantage of epicyclic gears is their robust design. They are easily converted into different ratios. They are also highly efficient. In addition, planetary gear trains can be designed to operate in multiple directions.
Another advantage of epicyclic gearing is their reduced size. They are often used for small-scale applications. The lower cost is associated with the reduced manufacturing time. Epicyclic gears should not be made on N/C milling machines. The epicyclic carrier should be cast and tooled on a single-purpose machine, which has several cutters cutting through material. The epicyclic carrier is smaller than the epicyclic gear.
Epicyclic gearing systems consist of three basic components: an input, an output, and a stationary component. The number of teeth in each gear determines the ratio of input rotation to output rotation. Typically, these gear sets are made of three separate pieces: the input gear, the output gear, and the stationary component. Depending on the size of the input and output gear, the ratio between the two components is greater than half.
They have higher gear ratios
The differences between epicyclic gears and regular, non-epicyclic gears are significant for many different applications. In particular, epicyclic gears have higher gear ratios. The reason behind this is that epicyclic gears require multiple mesh considerations. The epicyclic gears are designed to calculate the number of load application cycles per unit time. The sun gear, for example, is +1300 RPM. The planet gear, on the other hand, is +1700 RPM. The ring gear is also +1400 RPM, as determined by the number of teeth in each gear.
Torque is the twisting force of a gear, and the bigger the gear, the higher the torque. However, since the torque is also proportional to the size of the gear, bigger radii result in lower torque. In addition, smaller radii do not move cars faster, so the higher gear ratios do not move at highway speeds. The tradeoff between speed and torque is the gear ratio.
Planetary gears use multiple mechanisms to increase the gear ratio. Those using epicyclic gears have multiple gear sets, including a sun, a ring, and two planets. Moreover, the planetary gears are based on helical, bevel, and spur gears. In general, the higher gear ratios of epicyclic gears are superior to those of planetary gears.
Another example of planetary gears is the compound planet. This gear design has two different-sized gears on either end of a common casting. The large end engages the sun while the smaller end engages the annulus. The compound planets are sometimes necessary to achieve smaller steps in gear ratio. As with any gear, the correct alignment of planet pins is essential for proper operation. If the planets are not aligned properly, it may result in rough running or premature breakdown.


editor by CX 2023-05-22
China 1-12 Mod combined transmission Customized processing of C45 # steel stainless spur gear spiral bevel gear
Problem: New
Guarantee: Unavailable
Form: Cylindrical Equipment
Relevant Industries: Garment Outlets, Constructing Materials Retailers, Manufacturing Plant, Machinery Restore Shops, Foods & Beverage Manufacturing unit, Farms, Retail, Printing Stores, Construction works , Vitality & Mining, Meals & Beverage Stores, Advertising and marketing Business, Other
Excess weight (KG): 3
Showroom Location: Egypt, Canada, Turkey, United Kingdom, United States, Italy, France, Germany, Viet Nam, Philippines, Brazil, Peru, Saudi Arabia, Pakistan, Mexico, Russia, Spain, Thailand, F10 F12 F13 F06 Correct entrance axle generate shaft for BMW Morocco, Kenya, Argentina, South Korea, Chile, UAE, Colombia, Algeria, Sri Lanka, Romania, Bangladesh, South Africa, Kazakhstan, Ukraine, Kyrgyzstan, Nigeria, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Japan, Malaysia, Australia
Movie outgoing-inspection: Presented
Machinery Test Report: Offered
Marketing and advertising Type: New Solution 2571
Warranty of core components: Not Available
Core Elements: Engine, Bearing, Gearbox, Motor, Force vessel, Gear, Pump
Common or Nonstandard: Nonstandard
Tooth Profile: Spur
Content: C45 # Steel
Processing: Forging
Force Angle: 20
Software: steel plant, Agricultural machinery, Materials distribution
Module: 1-6 Mod 8 Mod 10 Mod 12 Mod
Specification: Tailored
Tooth Amount: Personalized
Service: OEM and ODM
MOQ: two hundred
Packing: Standard Packing
Warmth remedy: Normalizing
Certificate: RoHS
High quality: 100% Inspection
Packaging Details: Authentic carton packaging or Protecting packaging,wood pallets or wood circumstances if required
Port: HangZhou or ZheJiang
|

Spiral Gears for Right-Angle Right-Hand Drives
Spiral gears are used in mechanical systems to transmit torque. The bevel gear is a particular type of spiral gear. It is made up of two gears that mesh with one another. Both gears are connected by a bearing. The two gears must be in mesh alignment so that the negative thrust will push them together. If axial play occurs in the bearing, the mesh will have no backlash. Moreover, the design of the spiral gear is based on geometrical tooth forms.
Equations for spiral gear
The theory of divergence requires that the pitch cone radii of the pinion and gear be skewed in different directions. This is done by increasing the slope of the convex surface of the gear’s tooth and decreasing the slope of the concave surface of the pinion’s tooth. The pinion is a ring-shaped wheel with a central bore and a plurality of transverse axes that are offset from the axis of the spiral teeth.
Spiral bevel gears have a helical tooth flank. The spiral is consistent with the cutter curve. The spiral angle b is equal to the pitch cone’s genatrix element. The mean spiral angle bm is the angle between the genatrix element and the tooth flank. The equations in Table 2 are specific for the Spread Blade and Single Side gears from Gleason.
The tooth flank equation of a logarithmic spiral bevel gear is derived using the formation mechanism of the tooth flanks. The tangential contact force and the normal pressure angle of the logarithmic spiral bevel gear were found to be about twenty degrees and 35 degrees respectively. These two types of motion equations were used to solve the problems that arise in determining the transmission stationary. While the theory of logarithmic spiral bevel gear meshing is still in its infancy, it does provide a good starting point for understanding how it works.
This geometry has many different solutions. However, the main two are defined by the root angle of the gear and pinion and the diameter of the spiral gear. The latter is a difficult one to constrain. A 3D sketch of a bevel gear tooth is used as a reference. The radii of the tooth space profile are defined by end point constraints placed on the bottom corners of the tooth space. Then, the radii of the gear tooth are determined by the angle.
The cone distance Am of a spiral gear is also known as the tooth geometry. The cone distance should correlate with the various sections of the cutter path. The cone distance range Am must be able to correlate with the pressure angle of the flanks. The base radii of a bevel gear need not be defined, but this geometry should be considered if the bevel gear does not have a hypoid offset. When developing the tooth geometry of a spiral bevel gear, the first step is to convert the terminology to pinion instead of gear.
The normal system is more convenient for manufacturing helical gears. In addition, the helical gears must be the same helix angle. The opposite hand helical gears must mesh with each other. Likewise, the profile-shifted screw gears need more complex meshing. This gear pair can be manufactured in a similar way to a spur gear. Further, the calculations for the meshing of helical gears are presented in Table 7-1.
Design of spiral bevel gears
A proposed design of spiral bevel gears utilizes a function-to-form mapping method to determine the tooth surface geometry. This solid model is then tested with a surface deviation method to determine whether it is accurate. Compared to other right-angle gear types, spiral bevel gears are more efficient and compact. CZPT Gear Company gears comply with AGMA standards. A higher quality spiral bevel gear set achieves 99% efficiency.
A geometric meshing pair based on geometric elements is proposed and analyzed for spiral bevel gears. This approach can provide high contact strength and is insensitive to shaft angle misalignment. Geometric elements of spiral bevel gears are modeled and discussed. Contact patterns are investigated, as well as the effect of misalignment on the load capacity. In addition, a prototype of the design is fabricated and rolling tests are conducted to verify its accuracy.
The three basic elements of a spiral bevel gear are the pinion-gear pair, the input and output shafts, and the auxiliary flank. The input and output shafts are in torsion, the pinion-gear pair is in torsional rigidity, and the system elasticity is small. These factors make spiral bevel gears ideal for meshing impact. To improve meshing impact, a mathematical model is developed using the tool parameters and initial machine settings.
In recent years, several advances in manufacturing technology have been made to produce high-performance spiral bevel gears. Researchers such as Ding et al. optimized the machine settings and cutter blade profiles to eliminate tooth edge contact, and the result was an accurate and large spiral bevel gear. In fact, this process is still used today for the manufacturing of spiral bevel gears. If you are interested in this technology, you should read on!
The design of spiral bevel gears is complex and intricate, requiring the skills of expert machinists. Spiral bevel gears are the state of the art for transferring power from one system to another. Although spiral bevel gears were once difficult to manufacture, they are now common and widely used in many applications. In fact, spiral bevel gears are the gold standard for right-angle power transfer.While conventional bevel gear machinery can be used to manufacture spiral bevel gears, it is very complex to produce double bevel gears. The double spiral bevel gearset is not machinable with traditional bevel gear machinery. Consequently, novel manufacturing methods have been developed. An additive manufacturing method was used to create a prototype for a double spiral bevel gearset, and the manufacture of a multi-axis CNC machine center will follow.
Spiral bevel gears are critical components of helicopters and aerospace power plants. Their durability, endurance, and meshing performance are crucial for safety. Many researchers have turned to spiral bevel gears to address these issues. One challenge is to reduce noise, improve the transmission efficiency, and increase their endurance. For this reason, spiral bevel gears can be smaller in diameter than straight bevel gears. If you are interested in spiral bevel gears, check out this article.
Limitations to geometrically obtained tooth forms
The geometrically obtained tooth forms of a spiral gear can be calculated from a nonlinear programming problem. The tooth approach Z is the linear displacement error along the contact normal. It can be calculated using the formula given in Eq. (23) with a few additional parameters. However, the result is not accurate for small loads because the signal-to-noise ratio of the strain signal is small.
Geometrically obtained tooth forms can lead to line and point contact tooth forms. However, they have their limits when the tooth bodies invade the geometrically obtained tooth form. This is called interference of tooth profiles. While this limit can be overcome by several other methods, the geometrically obtained tooth forms are limited by the mesh and strength of the teeth. They can only be used when the meshing of the gear is adequate and the relative motion is sufficient.
During the tooth profile measurement, the relative position between the gear and the LTS will constantly change. The sensor mounting surface should be parallel to the rotational axis. The actual orientation of the sensor may differ from this ideal. This may be due to geometrical tolerances of the gear shaft support and the platform. However, this effect is minimal and is not a serious problem. So, it is possible to obtain the geometrically obtained tooth forms of spiral gear without undergoing expensive experimental procedures.
The measurement process of geometrically obtained tooth forms of a spiral gear is based on an ideal involute profile generated from the optical measurements of one end of the gear. This profile is assumed to be almost perfect based on the general orientation of the LTS and the rotation axis. There are small deviations in the pitch and yaw angles. Lower and upper bounds are determined as – 10 and -10 degrees respectively.
The tooth forms of a spiral gear are derived from replacement spur toothing. However, the tooth shape of a spiral gear is still subject to various limitations. In addition to the tooth shape, the pitch diameter also affects the angular backlash. The values of these two parameters vary for each gear in a mesh. They are related by the transmission ratio. Once this is understood, it is possible to create a gear with a corresponding tooth shape.
As the length and transverse base pitch of a spiral gear are the same, the helix angle of each profile is equal. This is crucial for engagement. An imperfect base pitch results in an uneven load sharing between the gear teeth, which leads to higher than nominal loads in some teeth. This leads to amplitude modulated vibrations and noise. In addition, the boundary point of the root fillet and involute could be reduced or eliminate contact before the tip diameter.


editor by czh 2023-05-08
China Professional Driven Gear CF800.37A. 106 10108003711060 spiral bevel gear
Product Description
1.Original parts
2.Good quality
3.Quick quotation
4.Reasonable price
5.Best service
Driven Gear CF80
Turbocharger,air filter,oil filter,air filter,starter,water pump,piston,pin,generator,fuel filter,ring,injector,pump,air comperssor,
connecting rod,connecting rod bearing,cylinder head gasket,cylinder sleeve,wiper motor,radiator,spark plug,engine cover
Changfa agricultural equipment
Wheeled tractor:
Crown A Series
CFA250/254/300/304/350/354
Product overview:
K Series
CFK1204/1304/1404/1504/1604
Crown C Series
CFC300/304/350/354/400/404/450/454
GB Series
CFG850B/854B/900B/904B/950B/954B/1000B/1004B/1100B/1104B/1204B
Crown D Series
CFD500/504/550/554/600/604
HA Series
CFH1100A/1104A/1204A/1304A
Crown F Series
CFF600/604/650/654/700/704/750/754/800/804
Rice transplanter:
4Line /6 Line Walking Transplanter
2ZS-4H/2ZS-4HD/2ZS-6
6Line / 8 Line High speed Ride-on Transplanter
2ZC-6
Tracked harvester:
6 series semi feeding crawler combine
CF603/604/604N/606/606N
8 Series Full Feeding Crawler Combine
CF803/804/805N
Wheeled harvester:
CF506 Wheeled Combine Harvester
4LZ-6
CF806 Wheeled Combine Harvester
4LZ-6
CF808 Wheeled Combine Harvester
4YZ-6
CF809 Combine harvester
4LZ-6
CF812 Wheeled Combine Harvester
cf812
CF904A Wheeled Combine Harvester
cf904
Diesel engine:
Crown Series Single Cylinder Diesel Engine
CF6(M),CF8(M),CF10(M),CF13(M),CF15(M),CF16(M),CF18(M),CF20(M),CF22(M),CF25(M),CF28(M),CF30(M),CF33(M),CF36(M),CF40(M)
Marine Series Single Cylinder Diesel Engine
CF15(M)-C,CF16(M)-C,CF18(M)-C,CF22(M)-C,CF25(M)-C,CF28(M)-C,CF30(M)-C
Single Cylinder Diesel Engine for Truck
CF1115A/CF1115AM
Water-cool evaporative big diesel engine
CF195(M),CF1100(M),CF1105(M),CF1110(M),CF1115(M),CF1115A(M),CF1125(M),CF1130(M),CF25(M),CF33(M),CF36(M)
Water cooled evaporative small diesel engine
CF170A,CF170,CF176,CF175(M),CF180(M),CF185(M),CF190(M),CF192(M),CF6,CF7(M),CF8(M),CF9(M),CF10(M),CF12(M),CF13(M),CF15(M)
Condensing cooled Diesel Engine series
CF175N(M),CF180N(M),CF185N(M),CF190N(M),CF192N(M),CF7N(M),CF8N(M),CF9N(M),CF10N(M),CF12N(M),CF13N(M),CF15N(M),CF16N(M) CF195N(M),CF1100N(M),CF1105N(M),CF1110N(M),CF1115N(M)
Forced water-cooled series
CF1110EM,CF1115EM,CF139BM,CF1125BM,CF1130BM,CF33BM,CF36BM
single cylinder air cooled diesel engines
CF170F,CF170FE,CF178F,CF178FE,CF180F,CF180FE,CF186F,CF186FE,CF188F,CF188FE,CF192F,CF192FE,CF195F
Walking tractor
CF91,CF101,CF101-1,CF101-2,CF101-3,CF101-4,CF101-5,CF101-6,CF121,CF121-1,CF121-2,CF121-3,CF121-4,CF151,CF151-1,CF151-3,CF151-4,CF151-5,GN121
B series multi cylinder diesel engine
CF3B25T/3B28T/3B30T/3B32T/4B35T/4B40T CF4B45T-Z/4B48T-Z/490QA/490QZ CY4F24Ti CF4B50T-Z/490Q
C SERIES MULTI CYLINDER DIESEL ENGINE
CF4102Q/4C60G/4C48D/4C56D/4C60D-Z/4C75D-Z
Generator:
Small Power Diesel Generator Set-Luxury type
CED6500S/CED6500S-ATS,CED6500S3/CED6500S3-ATS
Small Power Diesel Generator Set-Luxury type
CED6500WE
Small Power Diesel Generator Set-Luxury type
CED2500L(E)/CED2500X(E)/CED4000L(E)/CED4000X(E)/CED6500L(E)/CED6500X(E)/CED6500L(E)3/CED6500X(E)3
Small Power Diesel Generator Set-Luxury type
Small Power Diesel Generator Set
CED6500S/CED6500S-ATS/CED6500S3/CED6500S3-ATS
Big Power Diesel Generator Set
Small Power Diesel Generator Set-Luxury type
Water Pump Unit
| Type: | Driven Gear |
|---|---|
| Usage: | Driven Gear |
| Material: | Rail Steel |
| Power Source: | Diesel |
| Weight: | 1.3kg |
| Certification: | ISO/Ts 16949 |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How to Compare Different Types of Spur Gears
When comparing different types of spur gears, there are several important considerations to take into account. The main considerations include the following: Common applications, Pitch diameter, and Addendum circle. Here we will look at each of these factors in more detail. This article will help you understand what each type of spur gear can do for you. Whether you’re looking to power an electric motor or a construction machine, the right gear for the job will make the job easier and save you money in the long run.
Common applications
Among its many applications, a spur gear is widely used in airplanes, trains, and bicycles. It is also used in ball mills and crushers. Its high speed-low torque capabilities make it ideal for a variety of applications, including industrial machines. The following are some of the common uses for spur gears. Listed below are some of the most common types. While spur gears are generally quiet, they do have their limitations.
A spur gear transmission can be external or auxiliary. These units are supported by front and rear casings. They transmit drive to the accessory units, which in turn move the machine. The drive speed is typically between 5000 and 6000 rpm or 20,000 rpm for centrifugal breathers. For this reason, spur gears are typically used in large machinery. To learn more about spur gears, watch the following video.
The pitch diameter and diametral pitch of spur gears are important parameters. A diametral pitch, or ratio of teeth to pitch diameter, is important in determining the center distance between two spur gears. The center distance between two spur gears is calculated by adding the radius of each pitch circle. The addendum, or tooth profile, is the height by which a tooth projects above the pitch circle. Besides pitch, the center distance between two spur gears is measured in terms of the distance between their centers.
Another important feature of a spur gear is its low speed capability. It can produce great power even at low speeds. However, if noise control is not a priority, a helical gear is preferable. Helical gears, on the other hand, have teeth arranged in the opposite direction of the axis, making them quieter. However, when considering the noise level, a helical gear will work better in low-speed situations.
Construction
The construction of spur gear begins with the cutting of the gear blank. The gear blank is made of a pie-shaped billet and can vary in size, shape, and weight. The cutting process requires the use of dies to create the correct gear geometry. The gear blank is then fed slowly into the screw machine until it has the desired shape and size. A steel gear blank, called a spur gear billet, is used in the manufacturing process.
A spur gear consists of two parts: a centre bore and a pilot hole. The addendum is the circle that runs along the outermost points of a spur gear’s teeth. The root diameter is the diameter at the base of the tooth space. The plane tangent to the pitch surface is called the pressure angle. The total diameter of a spur gear is equal to the addendum plus the dedendum.
The pitch circle is a circle formed by a series of teeth and a diametrical division of each tooth. The pitch circle defines the distance between two meshed gears. The center distance is the distance between the gears. The pitch circle diameter is a crucial factor in determining center distances between two mating spur gears. The center distance is calculated by adding the radius of each gear’s pitch circle. The dedendum is the height of a tooth above the pitch circle.
Other considerations in the design process include the material used for construction, surface treatments, and number of teeth. In some cases, a standard off-the-shelf gear is the most appropriate choice. It will meet your application needs and be a cheaper alternative. The gear will not last for long if it is not lubricated properly. There are a number of different ways to lubricate a spur gear, including hydrodynamic journal bearings and self-contained gears.
Addendum circle
The pitch diameter and addendum circle are two important dimensions of a spur gear. These diameters are the overall diameter of the gear and the pitch circle is the circle centered around the root of the gear’s tooth spaces. The addendum factor is a function of the pitch circle and the addendum value, which is the radial distance between the top of the gear tooth and the pitch circle of the mating gear.
The pitch surface is the right-hand side of the pitch circle, while the root circle defines the space between the two gear tooth sides. The dedendum is the distance between the top of the gear tooth and the pitch circle, and the pitch diameter and addendum circle are the two radial distances between these two circles. The difference between the pitch surface and the addendum circle is known as the clearance.
The number of teeth in the spur gear must not be less than 16 when the pressure angle is twenty degrees. However, a gear with 16 teeth can still be used if its strength and contact ratio are within design limits. In addition, undercutting can be prevented by profile shifting and addendum modification. However, it is also possible to reduce the addendum length through the use of a positive correction. However, it is important to note that undercutting can happen in spur gears with a negative addendum circle.
Another important aspect of a spur gear is its meshing. Because of this, a standard spur gear will have a meshing reference circle called a Pitch Circle. The center distance, on the other hand, is the distance between the center shafts of the two gears. It is important to understand the basic terminology involved with the gear system before beginning a calculation. Despite this, it is essential to remember that it is possible to make a spur gear mesh using the same reference circle.
Pitch diameter
To determine the pitch diameter of a spur gear, the type of drive, the type of driver, and the type of driven machine should be specified. The proposed diametral pitch value is also defined. The smaller the pitch diameter, the less contact stress on the pinion and the longer the service life. Spur gears are made using simpler processes than other types of gears. The pitch diameter of a spur gear is important because it determines its pressure angle, the working depth, and the whole depth.
The ratio of the pitch diameter and the number of teeth is called the DIAMETRAL PITCH. The teeth are measured in the axial plane. The FILLET RADIUS is the curve that forms at the base of the gear tooth. The FULL DEPTH TEETH are the ones with the working depth equal to 2.000 divided by the normal diametral pitch. The hub diameter is the outside diameter of the hub. The hub projection is the distance the hub extends beyond the gear face.
A metric spur gear is typically specified with a Diametral Pitch. This is the number of teeth per inch of the pitch circle diameter. It is generally measured in inverse inches. The normal plane intersects the tooth surface at the point where the pitch is specified. In a helical gear, this line is perpendicular to the pitch cylinder. In addition, the pitch cylinder is normally normal to the helix on the outside.
The pitch diameter of a spur gear is typically specified in millimeters or inches. A keyway is a machined groove on the shaft that fits the key into the shaft’s keyway. In the normal plane, the pitch is specified in inches. Involute pitch, or diametral pitch, is the ratio of teeth per inch of diameter. While this may seem complicated, it’s an important measurement to understand the pitch of a spur gear.
Material
The main advantage of a spur gear is its ability to reduce the bending stress at the tooth no matter the load. A typical spur gear has a face width of 20 mm and will fail when subjected to 3000 N. This is far more than the yield strength of the material. Here is a look at the material properties of a spur gear. Its strength depends on its material properties. To find out what spur gear material best suits your machine, follow the following steps.
The most common material used for spur gears is steel. There are different kinds of steel, including ductile iron and stainless steel. S45C steel is the most common steel and has a 0.45% carbon content. This type of steel is easily obtainable and is used for the production of helical, spur, and worm gears. Its corrosion resistance makes it a popular material for spur gears. Here are some advantages and disadvantages of steel.
A spur gear is made of metal, plastic, or a combination of these materials. The main advantage of metal spur gears is their strength to weight ratio. It is about one third lighter than steel and resists corrosion. While aluminum is more expensive than steel and stainless steel, it is also easier to machine. Its design makes it easy to customize for the application. Its versatility allows it to be used in virtually every application. So, if you have a specific need, you can easily find a spur gear that fits your needs.
The design of a spur gear greatly influences its performance. Therefore, it is vital to choose the right material and measure the exact dimensions. Apart from being important for performance, dimensional measurements are also important for quality and reliability. Hence, it is essential for professionals in the industry to be familiar with the terms used to describe the materials and parts of a gear. In addition to these, it is essential to have a good understanding of the material and the dimensional measurements of a gear to ensure that production and purchase orders are accurate.


editor by CX 2023-04-20
China wholesaler CZPT 445-0609571 ATM Machine Spare Parts Dispenser 36t Gear 4450609571 bevel spiral gear
Product Description
CZPT ATM Machine Parts Dispenser 36T Gear
Specification:
| 1 | Brand | NCR |
| 2 | P/N | 4450609571 |
| 3 | Description | NCR Presenter 36T Gear |
| 4 | Usage | NCR ATM machines |
| 5 | Similar products | Full series of CZPT Nixdorf ATM parts |
| 6 | Inventory | Large quantity in stock |
| 7 | Factory location | HangZhou, China |
| 8 | Port | HangZhou, China |
Description:
| 1 | Quality | Grade A |
| 2 | Condition | Original new, refurbished and generic |
| 3 | Price | Negotiable, competitive price for different quantity |
| 4 | MOQ | 1 PC, small orders accept |
| 5 | Delivery time | 3-7 Working days after payment received |
| 6 | Service | 24 hours quick online response service |
| 7 | Warranty | 3 months |
| 8 | Payment terms | T/T, Western Union, PayPal |
Quality Control:
Adhering to the concept of “To develop by quality and trust”, CZPT Group takes the quality as our core, and strictly controls the quality according to the international standard, during each production process and before delivery.
Shipment:
| DHL | 3-6 days to arrive |
| TNT | 3-6 days to arrive |
| Fedex | 3-6 days to arrive |
| UPS | 3-6 days to arrive |
| EMS | 7-15 days to arrive |
| Others | By sea or air |
Our service
1. Supply full series of ATM whole machines and spare parts for NCR, Wincor, Diebold, NMD, Fujitsu, Hyosung, Hitachi,GRG, Kingteller, Eastcom and etc.
2. OEM accept, according to customers’ needs.
3. 24 hours professional and quick online technical support and solutions.
4. Providing technical consultation and training courses
5. After-sale service is reliable.
6. Prompt and on-time delivery.
| Certification: | CE, ISO |
|---|---|
| Shape: | Round |
| Safety: | Enclosed |
| Usage: | Through-The-Wall&Lobby |
| Brand: | NCR |
| Part Number: | 4450609571 |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Hypoid Bevel Vs Straight Spiral Bevel – What’s the Difference?
Spiral gears come in many different varieties, but there is a fundamental difference between a Hypoid bevel gear and a Straight spiral bevel. This article will describe the differences between the two types of gears and discuss their use. Whether the gears are used in industrial applications or at home, it is vital to understand what each type does and why it is important. Ultimately, your final product will depend on these differences.
Hypoid bevel gears
In automotive use, hypoid bevel gears are used in the differential, which allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds while maintaining the vehicle’s handling. This gearbox assembly consists of a ring gear and pinion mounted on a carrier with other bevel gears. These gears are also widely used in heavy equipment, auxiliary units, and the aviation industry. Listed below are some common applications of hypoid bevel gears.
For automotive applications, hypoid gears are commonly used in rear axles, especially on large trucks. Their distinctive shape allows the driveshaft to be located deeper in the vehicle, thus lowering the center of gravity and minimizing interior disruption. This design makes the hypoid gearset one of the most efficient types of gearboxes on the market. In addition to their superior efficiency, hypoid gears are very easy to maintain, as their mesh is based on sliding action.
The face-hobbed hypoid gears have a characteristic epicycloidal lead curve along their lengthwise axis. The most common grinding method for hypoid gears is the Semi-Completing process, which uses a cup-shaped grinding wheel to replace the lead curve with a circular arc. However, this method has a significant drawback – it produces non-uniform stock removal. Furthermore, the grinding wheel cannot finish all the surface of the tooth.
The advantages of a hypoid gear over a spiral bevel gear include a higher contact ratio and a higher transmission torque. These gears are primarily used in automobile drive systems, where the ratio of a single pair of hypoid gears is the highest. The hypoid gear can be heat-treated to increase durability and reduce friction, making it an ideal choice for applications where speed and efficiency are critical.
The same technique used in spiral bevel gears can also be used for hypoid bevel gears. This machining technique involves two-cut roughing followed by one-cut finishing. The pitch diameter of hypoid gears is up to 2500 mm. It is possible to combine the roughing and finishing operations using the same cutter, but the two-cut machining process is recommended for hypoid gears.
The advantages of hypoid gearing over spiral bevel gears are primarily based on precision. Using a hypoid gear with only three arc minutes of backlash is more efficient than a spiral bevel gear that requires six arc minutes of backlash. This makes hypoid gears a more viable choice in the motion control market. However, some people may argue that hypoid gears are not practical for automobile assemblies.
Hypoid gears have a unique shape – a cone that has teeth that are not parallel. Their pitch surface consists of two surfaces – a conical surface and a line-contacting surface of revolution. An inscribed cone is a common substitute for the line-contact surface of hypoid bevel gears, and it features point-contacts instead of lines. Developed in the early 1920s, hypoid bevel gears are still used in heavy truck drive trains. As they grow in popularity, they are also seeing increasing use in the industrial power transmission and motion control industries.
Straight spiral bevel gears
There are many differences between spiral bevel gears and the traditional, non-spiral types. Spiral bevel gears are always crowned and never conjugated, which limits the distribution of contact stress. The helical shape of the bevel gear is also a factor of design, as is its length. The helical shape has a large number of advantages, however. Listed below are a few of them.
Spiral bevel gears are generally available in pitches ranging from 1.5 to 2500 mm. They are highly efficient and are also available in a wide range of tooth and module combinations. Spiral bevel gears are extremely accurate and durable, and have low helix angles. These properties make them excellent for precision applications. However, some gears are not suitable for all applications. Therefore, you should consider the type of bevel gear you need before purchasing.
Compared to helical gears, straight bevel gears are easier to manufacture. The earliest method used to manufacture these gears was the use of a planer with an indexing head. However, with the development of modern manufacturing processes such as the Revacycle and Coniflex systems, manufacturers have been able to produce these gears more efficiently. Some of these gears are used in windup alarm clocks, washing machines, and screwdrivers. However, they are particularly noisy and are not suitable for automobile use.
A straight bevel gear is the most common type of bevel gear, while a spiral bevel gear has concave teeth. This curved design produces a greater amount of torque and axial thrust than a straight bevel gear. Straight teeth can increase the risk of breaking and overheating equipment and are more prone to breakage. Spiral bevel gears are also more durable and last longer than helical gears.
Spiral and hypoid bevel gears are used for applications with high peripheral speeds and require very low friction. They are recommended for applications where noise levels are essential. Hypoid gears are suitable for applications where they can transmit high torque, although the helical-spiral design is less effective for braking. For this reason, spiral bevel gears and hypoids are generally more expensive. If you are planning to buy a new gear, it is important to know which one will be suitable for the application.
Spiral bevel gears are more expensive than standard bevel gears, and their design is more complex than that of the spiral bevel gear. However, they have the advantage of being simpler to manufacture and are less likely to produce excessive noise and vibration. They also have less teeth to grind, which means that they are not as noisy as the spiral bevel gears. The main benefit of this design is their simplicity, as they can be produced in pairs, which saves money and time.
In most applications, spiral bevel gears have advantages over their straight counterparts. They provide more evenly distributed tooth loads and carry more load without surface fatigue. The spiral angle of the teeth also affects thrust loading. It is possible to make a straight spiral bevel gear with two helical axes, but the difference is the amount of thrust that is applied to each individual tooth. In addition to being stronger, the spiral angle provides the same efficiency as the straight spiral gear.
Hypoid gears
The primary application of hypoid gearboxes is in the automotive industry. They are typically found on the rear axles of passenger cars. The name is derived from the left-hand spiral angle of the pinion and the right-hand spiral angle of the crown. Hypoid gears also benefit from an offset center of gravity, which reduces the interior space of cars. Hypoid gears are also used in heavy trucks and buses, where they can improve fuel efficiency.
The hypoid and spiral bevel gears can be produced by face-hobbing, a process that produces highly accurate and smooth-surfaced parts. This process enables precise flank surfaces and pre-designed ease-off topographies. These processes also enhance the mechanical resistance of the gears by 15 to 20%. Additionally, they can reduce noise and improve mechanical efficiency. In commercial applications, hypoid gears are ideal for ensuring quiet operation.
Conjugated design enables the production of hypoid gearsets with length or profile crowning. Its characteristic makes the gearset insensitive to inaccuracies in the gear housing and load deflections. In addition, crowning allows the manufacturer to adjust the operating displacements to achieve the desired results. These advantages make hypoid gear sets a desirable option for many industries. So, what are the advantages of hypoid gears in spiral gears?
The design of a hypoid gear is similar to that of a conventional bevel gear. Its pitch surfaces are hyperbolic, rather than conical, and the teeth are helical. This configuration also allows the pinion to be larger than an equivalent bevel pinion. The overall design of the hypoid gear allows for large diameter shafts and a large pinion. It can be considered a cross between a bevel gear and a worm drive.
In passenger vehicles, hypoid gears are almost universal. Their smoother operation, increased pinion strength, and reduced weight make them a desirable choice for many vehicle applications. And, a lower vehicle body also lowers the vehicle’s body. These advantages made all major car manufacturers convert to hypoid drive axles. It is worth noting that they are less efficient than their bevel gear counterparts.
The most basic design characteristic of a hypoid gear is that it carries out line contact in the entire area of engagement. In other words, if a pinion and a ring gear rotate with an angular increment, line contact is maintained throughout their entire engagement area. The resulting transmission ratio is equal to the angular increments of the pinion and ring gear. Therefore, hypoid gears are also known as helical gears.


editor by CX 2023-04-18
China Precision Bevel Forging Gear For Differential Of Liberation Dongfeng Automobile bevel spiral gear
Problem: New
Warranty: Unavailable
Shape: BEVEL
Relevant Industries: Production Plant, Machinery Mend Outlets, Farms
Weight (KG): 10
Showroom Spot: None
Video clip outgoing-inspection: Presented
Equipment Check Report: Presented
Advertising and marketing Kind: New Product 2571
Guarantee of main elements: Much more than 5 a long time
Core Components: Gear
Tooth Profile: straight bevel gear
Direction: Remaining HAND
Materials: Metal, twenty GrMnTi
Processing: precision forging
Strain Angle: 20~30 degree
Regular or Nonstandard: Nonstandard
Outer Diameter: customized
Enamel number: OEM
Solution identify: Precision Bevel Forging Equipment For Differential Of Liberation Xihu (West Lake) Dis.feng
Search phrases: Precision Bevel Forging Gear
Measurement: Customzied
Services: OEM ODM
Quality: Higher Qaulity
Coloration: Black
MOQ: 10pcs
OEM: Take
Packaging Particulars: 1. Brush antirust oil 2. Internal packing: oil paper, Polyethylene bag, box 3. Outer packing: Wood circumstance or pallet 4. Tailored packing is also offered
Port: FOB HangZhou
Precision bevel forging gear for differential of Liberation Xihu (West Lake) Dis.feng automobile
Precision Bevel Forging Gear For Differential Of Liberation Xihu (West Lake) Dis.feng Car
| Specification: | straight bevel gear | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shape: | bevel | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| coloration: | normal | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Content: | Carbon Metal: 1571,1040,1045,1055,C35,C60, A105,LF2,S355J2G3,16Mn,20Mn~60Mn | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Force: | twenty~30 diploma | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tolerance: | ±0.pcs.Our primary equipments are a hundred and sixty,three hundred,four hundred,630,100T forging and stamping machines, much more than 50 processing equipments and 6 CNC equipment.We have obtained I S O 9 1 and T S 1 6 9 4 9 certificates.Welcome you to selecte a existing product from our catalogue or find engineering assistance for your software, you also can talk to our salesman about your sourcing specifications.We welcome new and previous consumers from all walks of lifestyle to speak to us for long term organization interactions and mutual good results! Creation Process Order Method 1.Feedback within 24 hours right after acquiring the inquire. 2.Acceptance of the prototype and little amount. 3.12 several hours each day on line. four.OEM and ODM provider. five.1-station service: From layout,to raw substance, to complete product. six.Self-owned Producing workshop. Packaging & Shipping FAQ Q1:What prorudcts Sanjin Gear can Source? 1.Substantial Good quality Straight Bevel Equipment.2.Transmission Gears for Tractor/Truck/Agriculture Machinery……3.Building Machinery Machining Components Q2:What is gain of SXIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.N Gear?1.Equipment Creation Line:Proven in the year of 2002. Q3:Why Pick HangZhou Sanjin Equipment in China?1.Exceptional Operation: Expert Marketing and advertising Group For Customer Drawing and Samples.2.Excellent Quality Management: Geared up with Stick Quality manage adhering to with Seasoned Engineers. 3.Excellent Value Conserving: Tiny Demo Great deal Buy Offered.4.Superb Following Product sales Monitoring System: Supply Every single Pictures,Supply and Maketing Information sharing. Q4: What delivery ways our use?A4:Typically talking, we will use UPS or DHL to ship the products. Our buyers can attain the goods inside 3 times.If our clients do not want them urgently, we will also use Fedex and TNT.If the items are of large excess weight and huge volumn, we will ship them by sea. This way can conserve our customers a whole lot of cash If you did not locate the product you might be fascinated in on our internet site. Remember to feel free of charge to enable me know. We are specially skilled in producing according to your sample or drawings. .
How to Compare Different Types of Spur GearsWhen comparing different types of spur gears, there are several important considerations to take into account. The main considerations include the following: Common applications, Pitch diameter, and Addendum circle. Here we will look at each of these factors in more detail. This article will help you understand what each type of spur gear can do for you. Whether you’re looking to power an electric motor or a construction machine, the right gear for the job will make the job easier and save you money in the long run. Common applicationsAmong its many applications, a spur gear is widely used in airplanes, trains, and bicycles. It is also used in ball mills and crushers. Its high speed-low torque capabilities make it ideal for a variety of applications, including industrial machines. The following are some of the common uses for spur gears. Listed below are some of the most common types. While spur gears are generally quiet, they do have their limitations. ConstructionThe construction of spur gear begins with the cutting of the gear blank. The gear blank is made of a pie-shaped billet and can vary in size, shape, and weight. The cutting process requires the use of dies to create the correct gear geometry. The gear blank is then fed slowly into the screw machine until it has the desired shape and size. A steel gear blank, called a spur gear billet, is used in the manufacturing process. Addendum circleThe pitch diameter and addendum circle are two important dimensions of a spur gear. These diameters are the overall diameter of the gear and the pitch circle is the circle centered around the root of the gear’s tooth spaces. The addendum factor is a function of the pitch circle and the addendum value, which is the radial distance between the top of the gear tooth and the pitch circle of the mating gear. Pitch diameterTo determine the pitch diameter of a spur gear, the type of drive, the type of driver, and the type of driven machine should be specified. The proposed diametral pitch value is also defined. The smaller the pitch diameter, the less contact stress on the pinion and the longer the service life. Spur gears are made using simpler processes than other types of gears. The pitch diameter of a spur gear is important because it determines its pressure angle, the working depth, and the whole depth. MaterialThe main advantage of a spur gear is its ability to reduce the bending stress at the tooth no matter the load. A typical spur gear has a face width of 20 mm and will fail when subjected to 3000 N. This is far more than the yield strength of the material. Here is a look at the material properties of a spur gear. Its strength depends on its material properties. To find out what spur gear material best suits your machine, follow the following steps.
China Industrial Transmission Gear Reducer Short-Pitch 32A Precision General Hardware Motorcycle Conveyor Transmission Roller Chains for Industrial & Agricultural spiral bevel gearProduct Description
Standard Information
ROLLER CHAINRoller chain or bush roller chain is the variety of chain push most commonly utilized for transmission of mechanical electrical power on several sorts of domestic, industrial and agricultural equipment, like conveyors, wire- and tube-drawing devices, printing presses, autos, motorcycles, and bicycles. It is made up of a series of short cylindrical rollers held collectively by side links. It is pushed by a toothed wheel known as a sprocket. It is a simple, dependable, and efficient means of electrical power transmission. Development OF THE CHAIN Two different dimensions of roller chain, showing development. The roller chain design lowers friction when compared to easier types, ensuing in greater efficiency and considerably less wear. The unique electricity transmission chain kinds lacked rollers and bushings, with equally the inner and outer plates held by pins which straight contacted the sprocket enamel nonetheless this configuration exhibited extremely quick dress in of equally the sprocket tooth, and the plates the place they pivoted on the pins. This difficulty was partly solved by the advancement of bushed chains, with the pins keeping the outer plates passing via bushings or sleeves connecting the inner plates. This dispersed the wear above a greater location however the tooth of the sprockets still wore much more rapidly than is fascinating, from the sliding friction against the bushings. The addition of rollers surrounding the bushing sleeves of the chain and supplied rolling make contact with with the tooth of the sprockets ensuing in superb resistance to put on of each sprockets and chain as well. There is even really lower friction, as long as the chain is adequately lubricated. Steady, clean, lubrication of roller chains is of major importance for successful procedure as well as proper tensioning. VARIANTS Design Format of a roller chain: 1. Outer plate, 2. Internal plate, 3. Pin, 4. Bushing, 5. Roller Roller chain is created in several sizes, the most widespread American Nationwide Standards Institute (ANSI) expectations getting 40, 50, sixty, and eighty. The 1st digit(s) show the pitch of the chain in eighths of an inch, with the very last digit getting 0 for normal chain, 1 for lightweight chain, and 5 for bushed chain with no rollers. As a result, a chain with 50 percent-inch pitch would be a #forty while a #160 sprocket would have enamel spaced 2 inches apart, and so forth. Metric pitches are expressed in sixteenths of an inch as a result a metric #8 chain (08B-1) would be equivalent to an ANSI #40. Most roller chain is created from simple carbon or alloy metal, but stainless metal is used in foodstuff processing equipment or other areas the place lubrication is a problem, and nylon or brass are from time to time seen for the same explanation. Roller chain is ordinarily hooked up making use of a master website link (also recognized as a connecting link), which typically has 1 pin held by a horseshoe clip relatively than friction match, enabling it to be inserted or taken off with straightforward equipment. Chain with a removable website link or pin is also recognized as cottered chain, which makes it possible for the size of the chain to be modified. 50 % backlinks (also acknowledged as offsets) are obtainable and are employed to boost the length of the chain by a single roller. Riveted roller chain has the grasp url (also recognized as a connecting url) “riveted” or mashed on the finishes. These pins are manufactured to be tough and are not detachable. USE An illustration of 2 ‘ghost’ sprockets tensioning a triplex roller chain method Sea Harrier FA.2 ZA195 entrance (cold) vector thrust nozzle – the nozzle is rotated by a chain push from an air motor Wear
The result of wear on a roller chain is to improve the pitch (spacing of the hyperlinks), creating the chain to increase more time. Be aware that this is because of to use at the pivoting pins and bushes, not from real stretching of the steel (as does take place to some adaptable metal parts this kind of as the hand-brake cable of a motor motor vehicle). With modern chains it is strange for a chain (other than that of a bicycle) to put on until it breaks, given that a worn chain leads to the speedy onset of use on the enamel of the sprockets, with greatest failure being the decline of all the tooth on the sprocket. The sprockets (in distinct the scaled-down of the two) undergo a grinding movement that places a characteristic hook shape into the pushed face of the enamel. (This influence is manufactured even worse by a chain improperly tensioned, but is unavoidable no make a difference what treatment is taken). The worn enamel (and chain) no more time gives smooth transmission of energy and this might turn out to be evident from the sounds, the vibration or (in car engines using a timing chain) the variation in ignition timing observed with a timing light. The two sprockets and chain should be changed in these situations, considering that a new chain on worn sprockets will not last lengthy. Nevertheless, in considerably less severe cases it could be possible to save the larger of the 2 sprockets, since it is always the more compact 1 that suffers the most use. Only in quite light-fat applications this kind of as a bicycle, or in excessive circumstances of poor stress, will the chain usually bounce off the sprockets. The lengthening due to use of a chain is calculated by the subsequent formula: M = the size of a number of hyperlinks calculated S = the variety of back links measured P = Pitch In sector, it is typical to monitor the motion of the chain tensioner (regardless of whether guide or computerized) or the exact duration of a drive chain (one particular rule of thumb is to replace a roller chain which has elongated 3% on an adjustable drive or 1.5% on a fixed-center generate). A simpler method, especially ideal for the cycle or bike user, is to try to pull the chain away from the greater of the 2 sprockets, even though making certain the chain is taut. Any significant motion (e.g. producing it possible to see via a gap) almost certainly suggests a chain worn up to and beyond the restrict. Sprocket damage will outcome if the issue is disregarded. Sprocket wear cancels this impact, and could mask chain put on. CHAIN Toughness The most widespread evaluate of roller chain’s strength is tensile toughness. Tensile toughness signifies how considerably load a chain can withstand beneath a one-time load prior to breaking. Just as important as tensile energy is a chain’s tiredness power. The crucial factors in a chain’s exhaustion energy is the quality of steel utilised to manufacture the chain, the warmth remedy of the chain parts, the top quality of the pitch gap fabrication of the linkplates, and the type of shot plus the intensity of shot peen coverage on the linkplates. Other elements can contain the thickness of the linkplates and the design and style (contour) of the linkplates. The rule of thumb for roller chain operating on a continuous push is for the chain load to not exceed a mere 1/6 or 1/9 of the chain’s tensile power, dependent on the sort of master links utilized (press-in shape vs. slip-in shape)[quotation needed]. Roller chains working on a continuous generate beyond these thresholds can and typically do fail prematurely through linkplate tiredness failure. The standard bare minimum greatest strength of the ANSI 29.1 metal chain is twelve,five hundred x (pitch, in inches)two. X-ring and O-Ring chains greatly lower wear by indicates of inner lubricants, escalating chain existence. The interior lubrication is inserted by implies of a vacuum when riveting the chain with each other. CHAIN STHangZhouRDS Specifications businesses (these kinds of as ANSI and ISO) keep specifications for style, dimensions, and interchangeability of transmission chains. For example, the pursuing Desk exhibits info from ANSI regular B29.1-2011 (Precision Electrical power Transmission Roller Chains, Attachments, and Sprockets) designed by the American Culture of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). See the references[8][9][ten] for further information. ASME/ANSI B29.1-2011 Roller Chain Normal SizesSizePitchMaximum Roller DiameterMinimum Final Tensile StrengthMeasuring Load25
For mnemonic functions, underneath is another presentation of important proportions from the identical standard, expressed in fractions of an inch (which was part of the thinking guiding the decision of favored figures in the ANSI common):
Notes: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
US $47.97 / 10FT | |
100 10FT (Min. Order) |
###
| After-sales Service: | 7*24hours |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Control Mode: | Continuous Path Control |
| Drive Mode: | Mechanical |
| Application: | Welding, Loading, Forging, Textile Machinery, Garment Machinery, Conveyor |
| Condition: | New |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 30/Meter
1 Meter(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
|
ANSI NO |
160 |
DIN/ISO NO: |
32A |
|
Pitch (mm): |
50.8000 |
Roller Diameter(mm): |
28.58 |
|
Inner Plate Width (mm): |
31.55 |
Average Tensile Strength: |
278.9KN |
|
Plate Thickness (mm) |
6.40 |
Pin Diameter(mm): |
14.27 |
|
Weight / Meter (kgs/m): |
10.10 |
Chain Size: |
5F, 10F, 5Meters |
|
Origin: |
Qingdao China |
HS Code: |
7315119000 |
###
| ASME/ANSI B29.1-2011 Roller Chain Standard Sizes | ||||
| Size | Pitch | Maximum Roller Diameter | Minimum Ultimate Tensile Strength | Measuring Load |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 0.250 in (6.35 mm) | 0.130 in (3.30 mm) | 780 lb (350 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 35 | 0.375 in (9.53 mm) | 0.200 in (5.08 mm) | 1,760 lb (800 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 41 | 0.500 in (12.70 mm) | 0.306 in (7.77 mm) | 1,500 lb (680 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 40 | 0.500 in (12.70 mm) | 0.312 in (7.92 mm) | 3,125 lb (1,417 kg) | 31 lb (14 kg) |
| 50 | 0.625 in (15.88 mm) | 0.400 in (10.16 mm) | 4,880 lb (2,210 kg) | 49 lb (22 kg) |
| 60 | 0.750 in (19.05 mm) | 0.469 in (11.91 mm) | 7,030 lb (3,190 kg) | 70 lb (32 kg) |
| 80 | 1.000 in (25.40 mm) | 0.625 in (15.88 mm) | 12,500 lb (5,700 kg) | 125 lb (57 kg) |
| 100 | 1.250 in (31.75 mm) | 0.750 in (19.05 mm) | 19,531 lb (8,859 kg) | 195 lb (88 kg) |
| 120 | 1.500 in (38.10 mm) | 0.875 in (22.23 mm) | 28,125 lb (12,757 kg) | 281 lb (127 kg) |
| 140 | 1.750 in (44.45 mm) | 1.000 in (25.40 mm) | 38,280 lb (17,360 kg) | 383 lb (174 kg) |
| 160 | 2.000 in (50.80 mm) | 1.125 in (28.58 mm) | 50,000 lb (23,000 kg) | 500 lb (230 kg) |
| 180 | 2.250 in (57.15 mm) | 1.460 in (37.08 mm) | 63,280 lb (28,700 kg) | 633 lb (287 kg) |
| 200 | 2.500 in (63.50 mm) | 1.562 in (39.67 mm) | 78,175 lb (35,460 kg) | 781 lb (354 kg) |
| 240 | 3.000 in (76.20 mm) | 1.875 in (47.63 mm) | 112,500 lb (51,000 kg) | 1,000 lb (450 kg |
###
| Pitch (inches) | Pitch expressed in eighths |
ANSI standard chain number |
Width (inches) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1⁄4 | 2⁄8 | 25 | 1⁄8 |
| 3⁄8 | 3⁄8 | 35 | 3⁄16 |
| 1⁄2 | 4⁄8 | 41 | 1⁄4 |
| 1⁄2 | 4⁄8 | 40 | 5⁄16 |
| 5⁄8 | 5⁄8 | 50 | 3⁄8 |
| 3⁄4 | 6⁄8 | 60 | 1⁄2 |
| 1 | 8⁄8 | 80 | 5⁄8 |
|
US $47.97 / 10FT | |
100 10FT (Min. Order) |
###
| After-sales Service: | 7*24hours |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Control Mode: | Continuous Path Control |
| Drive Mode: | Mechanical |
| Application: | Welding, Loading, Forging, Textile Machinery, Garment Machinery, Conveyor |
| Condition: | New |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 30/Meter
1 Meter(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
|
ANSI NO |
160 |
DIN/ISO NO: |
32A |
|
Pitch (mm): |
50.8000 |
Roller Diameter(mm): |
28.58 |
|
Inner Plate Width (mm): |
31.55 |
Average Tensile Strength: |
278.9KN |
|
Plate Thickness (mm) |
6.40 |
Pin Diameter(mm): |
14.27 |
|
Weight / Meter (kgs/m): |
10.10 |
Chain Size: |
5F, 10F, 5Meters |
|
Origin: |
Qingdao China |
HS Code: |
7315119000 |
###
| ASME/ANSI B29.1-2011 Roller Chain Standard Sizes | ||||
| Size | Pitch | Maximum Roller Diameter | Minimum Ultimate Tensile Strength | Measuring Load |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 0.250 in (6.35 mm) | 0.130 in (3.30 mm) | 780 lb (350 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 35 | 0.375 in (9.53 mm) | 0.200 in (5.08 mm) | 1,760 lb (800 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 41 | 0.500 in (12.70 mm) | 0.306 in (7.77 mm) | 1,500 lb (680 kg) | 18 lb (8.2 kg) |
| 40 | 0.500 in (12.70 mm) | 0.312 in (7.92 mm) | 3,125 lb (1,417 kg) | 31 lb (14 kg) |
| 50 | 0.625 in (15.88 mm) | 0.400 in (10.16 mm) | 4,880 lb (2,210 kg) | 49 lb (22 kg) |
| 60 | 0.750 in (19.05 mm) | 0.469 in (11.91 mm) | 7,030 lb (3,190 kg) | 70 lb (32 kg) |
| 80 | 1.000 in (25.40 mm) | 0.625 in (15.88 mm) | 12,500 lb (5,700 kg) | 125 lb (57 kg) |
| 100 | 1.250 in (31.75 mm) | 0.750 in (19.05 mm) | 19,531 lb (8,859 kg) | 195 lb (88 kg) |
| 120 | 1.500 in (38.10 mm) | 0.875 in (22.23 mm) | 28,125 lb (12,757 kg) | 281 lb (127 kg) |
| 140 | 1.750 in (44.45 mm) | 1.000 in (25.40 mm) | 38,280 lb (17,360 kg) | 383 lb (174 kg) |
| 160 | 2.000 in (50.80 mm) | 1.125 in (28.58 mm) | 50,000 lb (23,000 kg) | 500 lb (230 kg) |
| 180 | 2.250 in (57.15 mm) | 1.460 in (37.08 mm) | 63,280 lb (28,700 kg) | 633 lb (287 kg) |
| 200 | 2.500 in (63.50 mm) | 1.562 in (39.67 mm) | 78,175 lb (35,460 kg) | 781 lb (354 kg) |
| 240 | 3.000 in (76.20 mm) | 1.875 in (47.63 mm) | 112,500 lb (51,000 kg) | 1,000 lb (450 kg |
###
| Pitch (inches) | Pitch expressed in eighths |
ANSI standard chain number |
Width (inches) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1⁄4 | 2⁄8 | 25 | 1⁄8 |
| 3⁄8 | 3⁄8 | 35 | 3⁄16 |
| 1⁄2 | 4⁄8 | 41 | 1⁄4 |
| 1⁄2 | 4⁄8 | 40 | 5⁄16 |
| 5⁄8 | 5⁄8 | 50 | 3⁄8 |
| 3⁄4 | 6⁄8 | 60 | 1⁄2 |
| 1 | 8⁄8 | 80 | 5⁄8 |
The Difference Between Planetary Gears and Spur Gears
A spur gear is a type of mechanical drive that turns an external shaft. The angular velocity is proportional to the rpm and can be easily calculated from the gear ratio. However, to properly calculate angular velocity, it is necessary to know the number of teeth. Fortunately, there are several different types of spur gears. Here’s an overview of their main features. This article also discusses planetary gears, which are smaller, more robust, and more power-dense.
Planetary gears are a type of spur gear
One of the most significant differences between planetary gears and spurgears is the way that the two share the load. Planetary gears are much more efficient than spurgears, enabling high torque transfer in a small space. This is because planetary gears have multiple teeth instead of just one. They are also suitable for intermittent and constant operation. This article will cover some of the main benefits of planetary gears and their differences from spurgears.
While spur gears are more simple than planetary gears, they do have some key differences. In addition to being more basic, they do not require any special cuts or angles. Moreover, the tooth shape of spur gears is much more complex than those of planetary gears. The design determines where the teeth make contact and how much power is available. However, a planetary gear system will be more efficient if the teeth are lubricated internally.
In a planetary gear, there are three shafts: a sun gear, a planet carrier, and an external ring gear. A planetary gear is designed to allow the motion of one shaft to be arrested, while the other two work simultaneously. In addition to two-shaft operation, planetary gears can also be used in three-shaft operations, which are called temporary three-shaft operations. Temporary three-shaft operations are possible through frictional coupling.
Among the many benefits of planetary gears is their adaptability. As the load is shared between several planet gears, it is easier to switch gear ratios, so you do not need to purchase a new gearbox for every new application. Another major benefit of planetary gears is that they are highly resistant to high shock loads and demanding conditions. This means that they are used in many industries.
They are more robust
An epicyclic gear train is a type of transmission that uses concentric axes for input and output. This type of transmission is often used in vehicles with automatic transmissions, such as a Lamborghini Gallardo. It is also used in hybrid cars. These types of transmissions are also more robust than conventional planetary gears. However, they require more assembly time than a conventional parallel shaft gear.
An epicyclic gearing system has three basic components: an input, an output, and a carrier. The number of teeth in each gear determines the ratio of input rotation to output rotation. In some cases, an epicyclic gear system can be made with two planets. A third planet, known as the carrier, meshes with the second planet and the sun gear to provide reversibility. A ring gear is made of several components, and a planetary gear may contain many gears.
An epicyclic gear train can be built so that the planet gear rolls inside the pitch circle of an outer fixed gear ring, or “annular gear.” In such a case, the curve of the planet’s pitch circle is called a hypocycloid. When epicycle gear trains are used in combination with a sun gear, the planetary gear train is made up of both types. The sun gear is usually fixed, while the ring gear is driven.
Planetary gearing, also known as epicyclic gear, is more durable than other types of transmissions. Because planets are evenly distributed around the sun, they have an even distribution of gears. Because they are more robust, they can handle higher torques, reductions, and overhung loads. They are also more energy-dense and robust. In addition, planetary gearing is often able to be converted to various ratios.
They are more power dense
The planet gear and ring gear of a compound planetary transmission are epicyclic stages. One part of the planet gear meshes with the sun gear, while the other part of the gear drives the ring gear. Coast tooth flanks are used only when the gear drive works in reversed load direction. Asymmetry factor optimization equalizes the contact stress safety factors of a planetary gear. The permissible contact stress, sHPd, and the maximum operating contact stress (sHPc) are equalized by asymmetry factor optimization.
In addition, epicyclic gears are generally smaller and require fewer space than helical ones. They are commonly used as differential gears in speed frames and in looms, where they act as a Roper positive let off. They differ in the amount of overdrive and undergearing ratio they possess. The overdrive ratio varies from fifteen percent to forty percent. In contrast, the undergearing ratio ranges from 0.87:1 to 69%.
The TV7-117S turboprop engine gearbox is the first known application of epicyclic gears with asymmetric teeth. This gearbox was developed by the CZPT Corporation for the Ilyushin Il-114 turboprop plane. The TV7-117S’s gearbox arrangement consists of a first planetary-differential stage with three planet gears and a second solar-type coaxial stage with five planet gears. This arrangement gives epicyclic gears the highest power density.
Planetary gearing is more robust and power-dense than other types of gearing. They can withstand higher torques, reductions, and overhung loads. Their unique self-aligning properties also make them highly versatile in rugged applications. It is also more compact and lightweight. In addition to this, epicyclic gears are easier to manufacture than planetary gears. And as a bonus, they are much less expensive.
They are smaller
Epicyclic gears are small mechanical devices that have a central “sun” gear and one or more outer intermediate gears. These gears are held in a carrier or ring gear and have multiple mesh considerations. The system can be sized and speeded by dividing the required ratio by the number of teeth per gear. This process is known as gearing and is used in many types of gearing systems.
Planetary gears are also known as epicyclic gearing. They have input and output shafts that are coaxially arranged. Each planet contains a gear wheel that meshes with the sun gear. These gears are small and easy to manufacture. Another advantage of epicyclic gears is their robust design. They are easily converted into different ratios. They are also highly efficient. In addition, planetary gear trains can be designed to operate in multiple directions.
Another advantage of epicyclic gearing is their reduced size. They are often used for small-scale applications. The lower cost is associated with the reduced manufacturing time. Epicyclic gears should not be made on N/C milling machines. The epicyclic carrier should be cast and tooled on a single-purpose machine, which has several cutters cutting through material. The epicyclic carrier is smaller than the epicyclic gear.
Epicyclic gearing systems consist of three basic components: an input, an output, and a stationary component. The number of teeth in each gear determines the ratio of input rotation to output rotation. Typically, these gear sets are made of three separate pieces: the input gear, the output gear, and the stationary component. Depending on the size of the input and output gear, the ratio between the two components is greater than half.
They have higher gear ratios
The differences between epicyclic gears and regular, non-epicyclic gears are significant for many different applications. In particular, epicyclic gears have higher gear ratios. The reason behind this is that epicyclic gears require multiple mesh considerations. The epicyclic gears are designed to calculate the number of load application cycles per unit time. The sun gear, for example, is +1300 RPM. The planet gear, on the other hand, is +1700 RPM. The ring gear is also +1400 RPM, as determined by the number of teeth in each gear.
Torque is the twisting force of a gear, and the bigger the gear, the higher the torque. However, since the torque is also proportional to the size of the gear, bigger radii result in lower torque. In addition, smaller radii do not move cars faster, so the higher gear ratios do not move at highway speeds. The tradeoff between speed and torque is the gear ratio.
Planetary gears use multiple mechanisms to increase the gear ratio. Those using epicyclic gears have multiple gear sets, including a sun, a ring, and two planets. Moreover, the planetary gears are based on helical, bevel, and spur gears. In general, the higher gear ratios of epicyclic gears are superior to those of planetary gears.
Another example of planetary gears is the compound planet. This gear design has two different-sized gears on either end of a common casting. The large end engages the sun while the smaller end engages the annulus. The compound planets are sometimes necessary to achieve smaller steps in gear ratio. As with any gear, the correct alignment of planet pins is essential for proper operation. If the planets are not aligned properly, it may result in rough running or premature breakdown.


editor by czh 2023-01-31